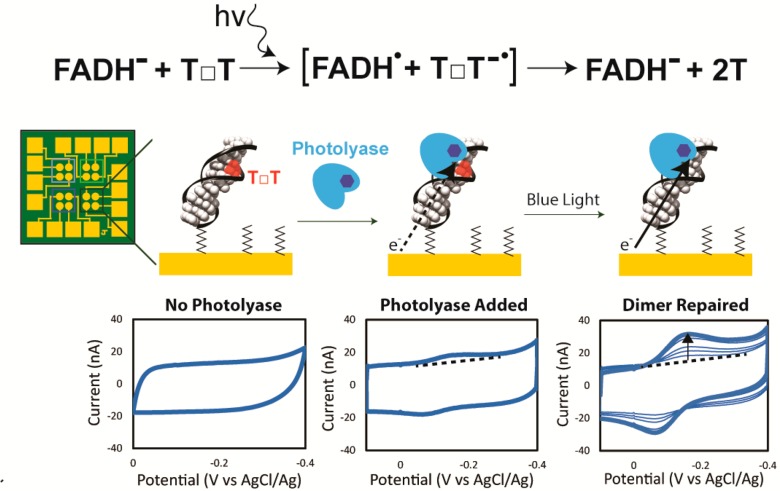
Figure 1.
Cyclic voltammetry of thymine dimer repair by photolyase. (Top) Reductive catalytic cycle of the flavin cofactor in photolyase to repair thymine dimers. (Bottom) Cyclic voltammetry on multiplexed chip electrodes modified with 29 bp dsDNA and backfilled with mercaptohexanol. The reaction cartoon on the electrode is shown above with corresponding CV below. (Left) Monolayer of duplex DNA (29 bp), each with a single thymine dimer (red T□T), is scanned anaerobically at 100 mV/s in Tris buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM KCl, 1 mM EDTA, 10% glycerol, pH 7.5). (Center) Addition of E. coli photolyase (50 μM) shows a small flavin redox peak centered around −100 mV vs AgCl/Ag, which is consistent with the fully reduced flavin. (Right) Irradiation with blue light repairs the thymine dimer over time and increases the yield of charge transferred through the DNA duplex to and from the flavin. After subtracting the background current (dotted line), the area under the reductive peak can be integrated to give the total charge transferred to the flavin.