Figure 7.
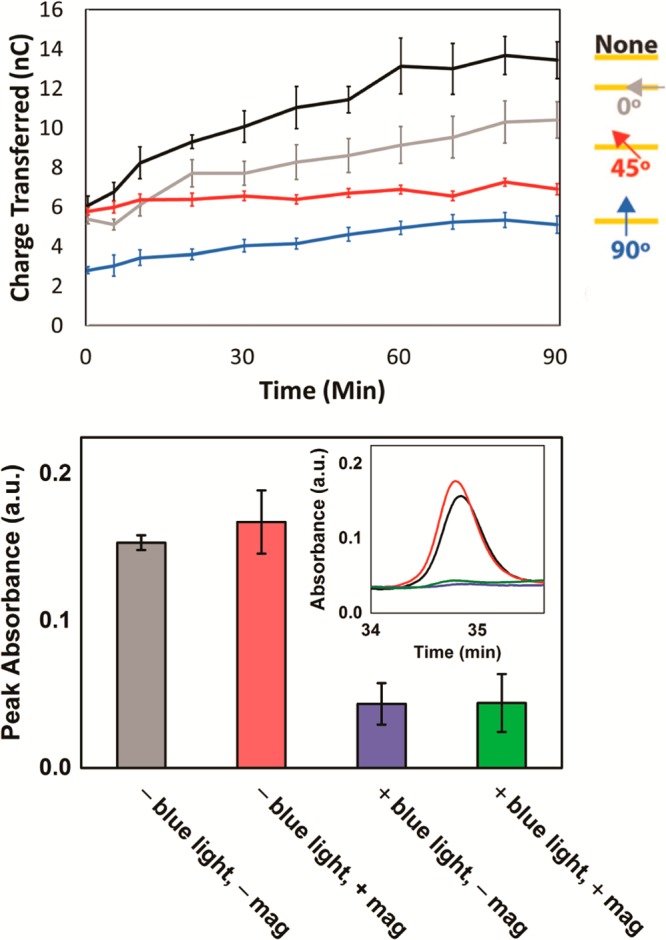
Monitoring CPD repair by cryptochrome (AtCRY1ΔC). (Top) Electrochemical experiments show the total amount of charge transferred to the flavin of AtCRY1ΔC over time irradiated with varying magnetic field angles. 50 μM cryptochrome was added to a monolayer of 29 bp dsDNA with T□T and irradiated with blue light (t = 0) anaerobically in Tris buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM KCl, 1 mM EDTA, 10% glycerol, pH 7.5). The background magnetic field was 0.4 G, and the applied field was added to this to give the total field strength of 30 G. The magnetic field angle was varied by applying the magnetic field at either a 0°, 45°, or 90° angle relative to the plane of the electrode surface. Standard error was plotted with n = 4. (Bottom) Monitoring CPD repair with AtCRY1ΔC by HPLC. Duplex DNA containing T□T was incubated under anaerobic conditions in solution for 1 h at ambient temperature with AtCRY1ΔC with and without a 6600 G magnetic field, and in the presence or absence of blue light. Phosphodiesterase I was then used to digest the DNA, and the HPLC peak characteristic of the thymine dimer (inset) was quantified and compared.
