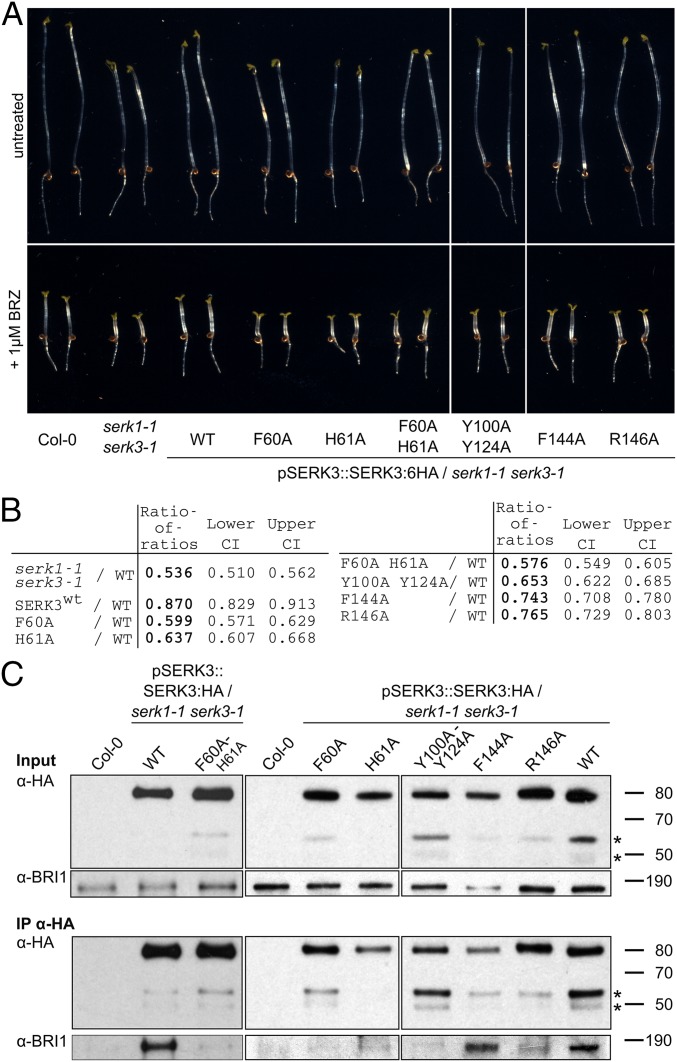
Fig. 2.
Mutations in the SERK3 ligand binding and receptor interfaces differentially impact SERK3 function and complex formation in vivo. (A) Hypocotyl growth assay in the presence and absence of the brassinosteroid biosynthesis inhibitor brassinazole (BRZ), from seedlings grown for 5 d in the dark. Serk1-1 serk3-1 mutants are BRZ hypersensitive and this phenotype can be complemented by expressing SERK3 in the mutant background (Col-0, untransformed wild type, n = 50). (B) Quantification of the data from A. The log-transformed endpoint hypocotyl length was analyzed by a mixed effects model for the ratio of the transgenic lines vs. wild type, allowing for heterogeneous variances. The ratio of the untreated and BRZ-treated hypocotyl length was calculated for wild type (rwt) and each mutant line (rm); the ratio of this ratio for wild type divided by the ratio for a given mutant line results in the ratio of ratios (RR = rwt/rm; CI, confidence interval). (C) Coimmunoprecipitation (Co-IP) of lines shown in A. SERK3:HA was immunoprecipitated from plant protein extracts using an anti-HA antibody (IP-HA) and BRI1 was detected with an anti-BRI1 antibody (14) in the IP elution.