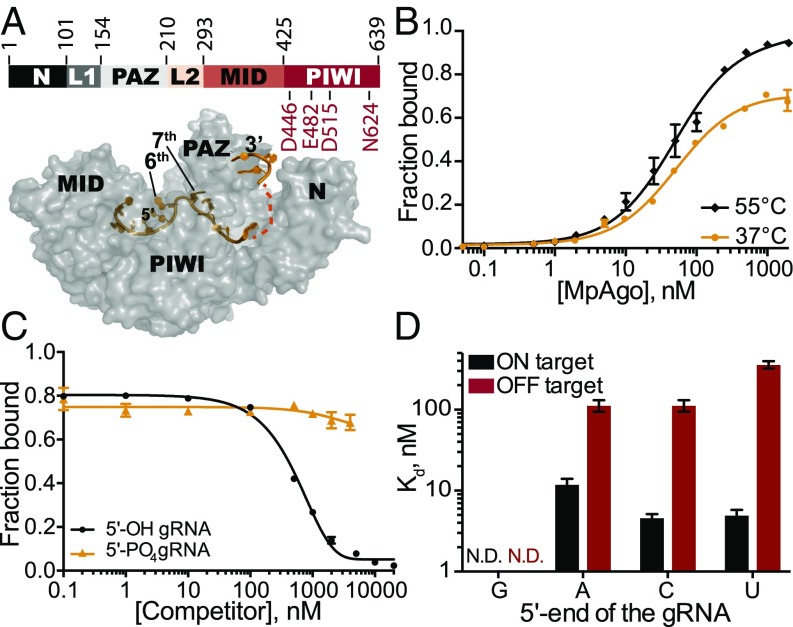
Fig. 1.
Stability and specificity of in vitro reconstituted MpAgo RNPs. (A, Top) Organization of MpAgo’s domains and (A, Bottom) the structure (PDB ID: 5I4A) of MpAgo (gray) bound to its guide RNA (gRNA, orange). The bilobed structure includes a PAZ (PIWI-Argonaute-Zwille) domain that anchors the 3′-end of the gRNA, whereas the second lobe includes a MID and a PIWI domain that binds the 5′ end of the gRNA, and includes the catalytic residues, as marked. The gRNA bound to MpAgo is bent at the sixth and seventh nts. (B) MpAgo binding of gRNA at two temperatures: 37 °C (orange) and 55 °C (black). The fraction of bound gRNA is plotted as a function of MpAgo concentration. The data fit with a standard binding isotherm (solid lines) yield Kd values at 37 °C and 55 °C of 52 ± 4 nM and 49 ± 5 nM, respectively. Data are represented as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. (C) Competition-binding assay at 37 °C to examine displacement of gRNA from the MpAgo RNP complex, with 5′-OH RNA competitor (black) and 5′-PO4 RNA competitor (orange). The adjusted half-inhibitory concentrations (IC50) are 0.25 ± 0.08 μM and >4.5 μM for the 5′-OH RNA and 5′-PO4 RNA competitors, respectively. Data are represented as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. (D) Substrate ssRNA filter-binding assays with catalytically inactive MpAgo RNP formed with a 5′-G, 5′-A, 5′-U, or 5′-C gRNA and either fully complementary substrate (ON target, black) or noncomplementary ssRNA substrate (OFF target, red) in the presence of 2 μg/mL heparin. The obtained average Kd values are plotted as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. N.D., not detected.