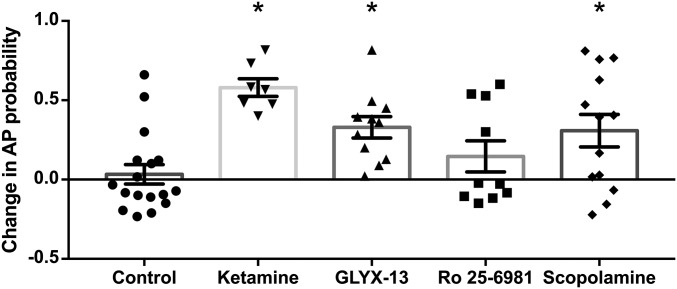
Fig. 5.
Summary of the effects of rapid antidepressants on synaptically driven APs. Ketamine, GLYX-13, and scopolamine significantly increase the synaptic AP probability compared with baseline (ketamine and GLYX-13, P < 0.001 and scopolamine, P < 0.05), indicating pyramidal cells are disinhibited. Conversely, the GluN2B subunit-selective NMDAR antagonist Ro 25-6981 does not alter synaptically driven pyramidal cell excitability. Replotted from Figs. 1–4. Asterisks indicate a significant difference from baseline and drug for each inhibitor. All values are mean ± SEM.