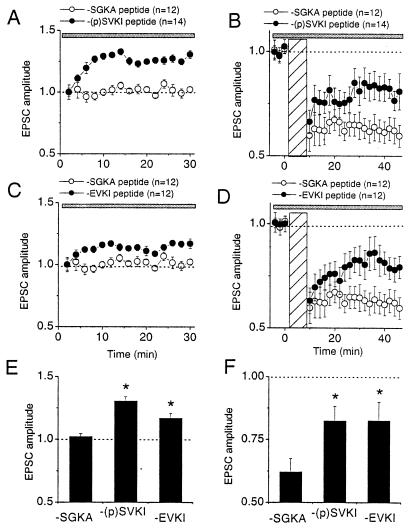
Figure 5.
Intracellular perfusion of GluR2/3 C-terminal peptides that selectively disrupt GluR2–PICK1 interaction affects the basal synaptic transmission and inhibits expression of LTD. (A) Effect of the phosphopeptide KKEGYNVYGIES-(PO4)-VKI (−(p)SVKI, 200 μM, ●) on the basal synaptic transmission. (B) Effect of −(p)SVKI peptide on LTD induction compared with the control peptide. The LTD experiments in B were continuations of the baseline recordings in A. (C) Effect of KKEGYNVYGIESVKI peptide (−EVKI, 200 μM, ●) on the basal synaptic transmission. (D) Effect of −EVKI peptide on LTD induction compared with that of the control peptide. The LTD experiments in D were continuations of the baseline recordings in C. (E) The amplitude histogram of basal EPSCs at 30 min after perfusion. * indicates the significance at α = 0.05 (ANOVA, single factor). (F) The amplitude histogram of LTD at 30 min after pairing. * indicates the group whose mean is significantly different from those of controls, no peptide, or −SGKA peptide (Dunnett's test, α = 0.05). Gray bar indicates the period of postsynaptic application of peptides. Hatched bar indicates the period of pairing for LTD induction.