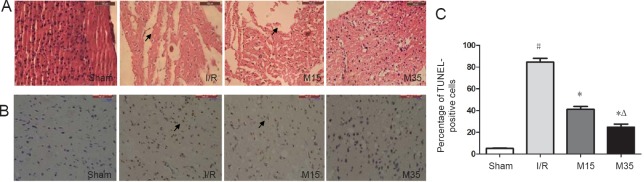
Figure 3.
Pathological changes and apoptotic cells in the injured brain.
(A) Photographs of brain sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin 3 days after reperfusion. Suspended moxibustion for 35 minutes alleviated the pathological changes. The arrows indicate cell loss. Scale bars: 100 μm. (B) Photographs of apoptotic cells (arrows) detected by the TUNEL assay 3 days after reperfusion in rats. The 35-minute moxibustion treatment decreased the total area of TUNEL-positive cells compared with the I/R and 15-minute moxibustion groups. Scale bars: 100 μm. (C) Quantitative analysis of the percentage of TUNEL-positive cells, expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3) and analyzed by one-way analysis of variance followed by Dunnett's test. #P < 0.05, vs. sham group; *P < 0.05, vs. I/R group; ΔP < 0.05, vs. M15 group. Sham: Sham surgery group; I/R: I/R group; M15: 15-minute moxibustion group; M35: 35-minute moxibustion group. I/R: ischemia/reperfusion; TUNEL: terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling.