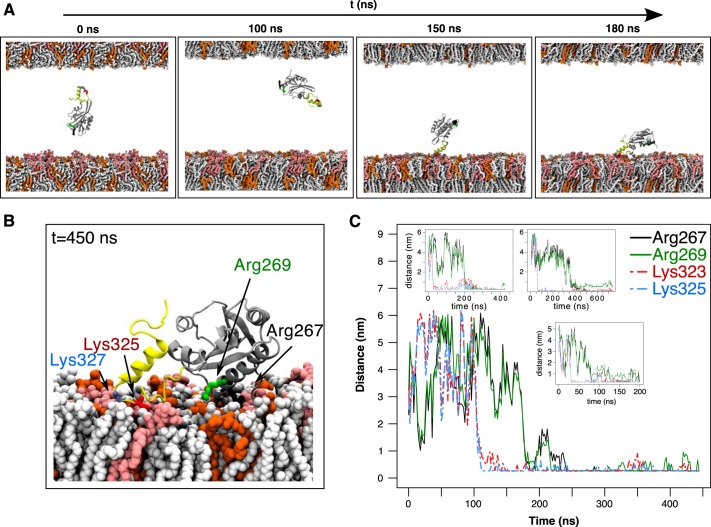
Figure 4.
Atomistic simulations to explore twinfilin-membrane interaction. A, snapshots from a simulation with the C-terminal ADF-H domain and the tail (TWF1(169–350)) together with a phosphoinositide-rich membrane (system 5 in Table S1). The lipid composition in the upper membrane leaflet was POPC:POPS:POPE 60:20:20, and that in the lower leaflet was POPC:POPS:POPE:PI(4,5)P2 50:20:20:10. The tail of twinfilin is shown in yellow, and PI(4,5)P2 in the membrane is depicted in light red. B, the final conformation of TWF1(169–350) on a membrane. PI(4,5)P2 in the membrane is depicted in light red. Two residues at the actin-binding region of the ADF-H domain (Arg-267 and Arg-269) and two residues in the twinfilin tail (Lys-325 and Lys-327) are highlighted. C, minimum distance between lipids of the PI(4,5)P2-rich leaflet and residues Arg-267, Arg-269, Lys-325, and Lys-327 during four independent simulations. Residues in the C-terminal tail (Lys-325 and Lys-327) equilibrated much faster onto the plasma membrane compared with the residues in the ADF-H domain (Arg-267 and Arg-269).