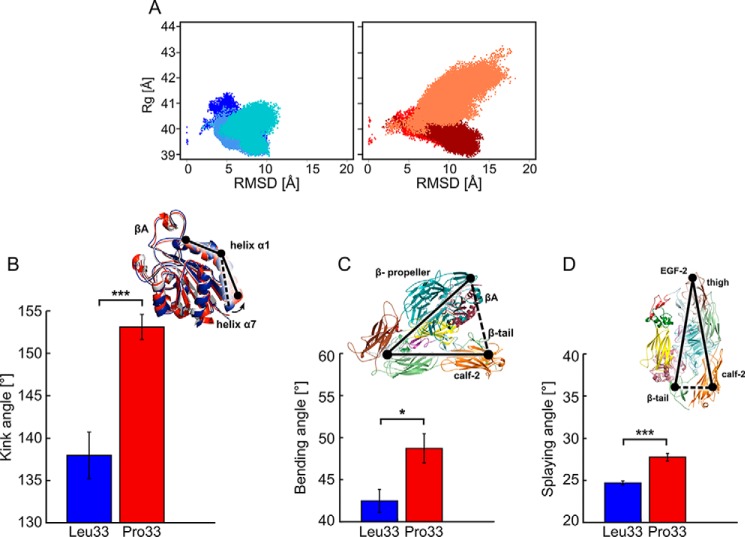
Figure 3.
Conformational changes of the Leu33 and Pro33 isoforms of αIIbβ3 during MD simulations. A, two-dimensional histogram of the RMSD of Cα atoms of the entire ectodomain after mass-weighted fitting on the β-propeller and βA domains of the starting structure versus Rg for the ectodomains. Bluish colors represent the three MD simulations of the Leu33 isoform, and reddish colors represent those of the Pro33 variant. B–D, histograms of the kink, bending, and splaying angles averaged over three MD simulations with error bars showing the S.E. and asterisks indicating the statistical significance (*, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.0001). Above the plots, the definitions of the angles are given: B, kink angles as black solid line connecting the three points (center of mass of Cα atoms of Lys112 and Ile118, center of mass of Cα atoms of Gln119 and Lys125, and center of mass of Cα atoms of Leu126 and Leu132) on both isoforms; C, bending angle as a black solid line connecting the three points (center of mass of the β-propeller and βA domains, center of mass of the PSI domain, and center of mass of the calf-2 and β-tail domains); D, splaying angle as a black solid line connecting the three points (center of mass of Cα atoms of Leu788 and Gly796 in the calf-2 domain, center of mass of the Cα atoms of Cys602 and Cys608 in the thigh domain, and center of mass of Cα atoms of Glu1557 and Val1561 in the β-tail domain).