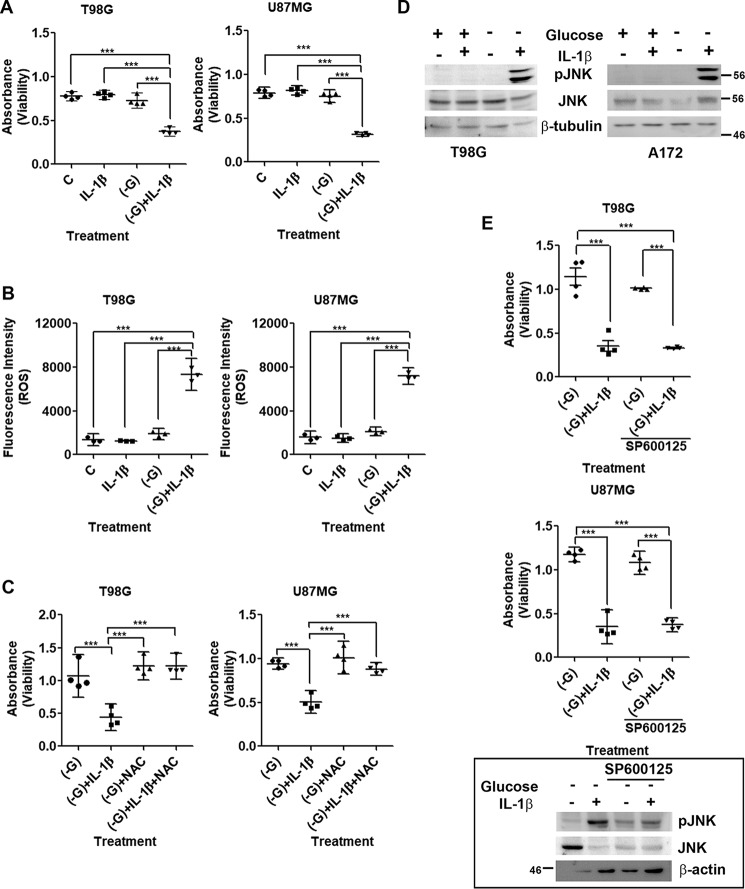
Figure 1.
Glucose starvation sensitizes glioma cells to IL-1β–induced apoptosis in a ROS-dependent manner. A, IL-1β induces glioma cell death under glucose deprivation. B, increase in DHE fluorescence intensity depicting heightened ROS generation in glucose-deprived IL-1β–treated cells. C, increase in absorbance representing rescue of cell death by the ROS inhibitor NAC. D, Western blots demonstrating increased pJNK levels in glioma cells treated with IL-1β in the absence of glucose. E, MTS assay showing JNK-independent cell death. The inset shows the efficacy of JNK inhibitor. The graphs represent scatter plots with each data point representing average absorbance values depicting glioma cell viability (A, C, and E) and average fluorescence intensities depicting ROS levels (B). −G denotes glucose-free DMEM. SP600125 is a JNK inhibitor. One-way ANOVA (Bonferroni's multiple comparison test) was used for statistical analysis. Error bars represent S.E. (n = 4 in A, C, and E; n = 3 in B). ***, p < 0.001.