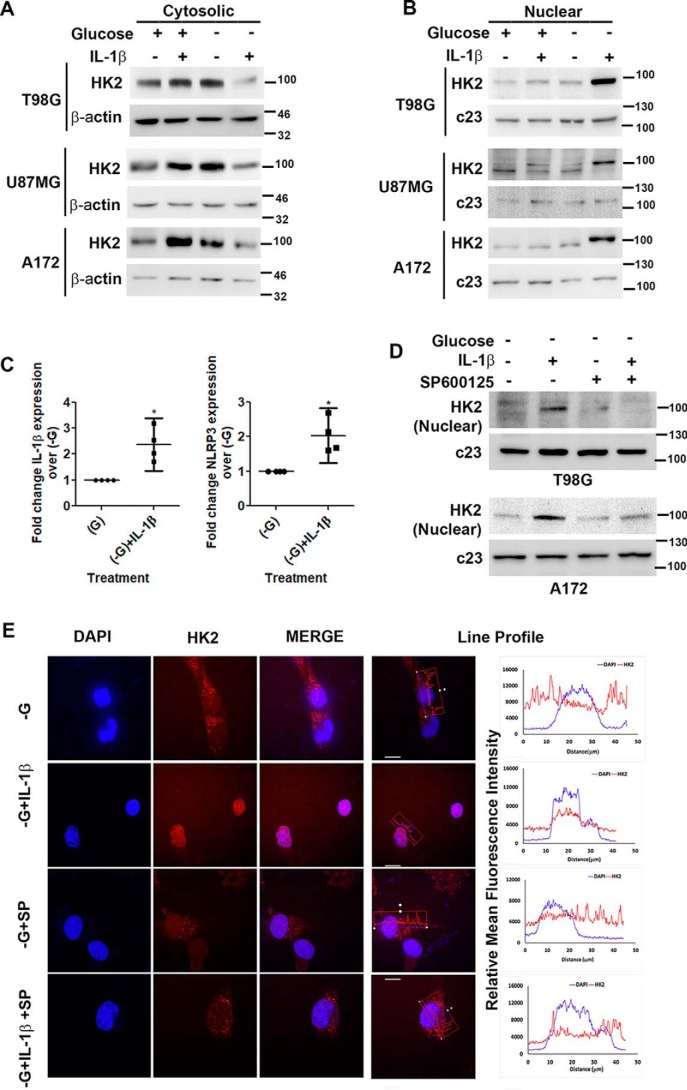
Figure 3.
IL-1β induces JNK-dependent nuclear localization of HK2. Shown are Western blots demonstrating cytosolic (A) and nuclear (B) HK2 levels in glioma cells treated with IL-1β in the presence or absence of glucose. C, qRT-PCR analysis shows increased IL-1β and NLRP3 mRNA levels in cells treated with IL-1β under glucose deprivation. Each data point in the scatter plots represents -fold change with respect to glucose-free DMEM (−G) from independent experiments (n = 4). D, Western blot demonstrating nuclear HK2 levels in cells treated with or without IL-1β or SP600125 in the presence or absence of glucose. Western blots are representative images of three independent experiments showing similar results. Blots were reprobed for β-actin or c23 to establish equivalent loading. E, JNK regulates nuclear localization of HK2. Immunofluorescence microscopy revealed nuclear HK2 localization in glucose-deprived cells in the presence of IL-1β. Treatment with JNK inhibitor (SP600125) prevented HK2 localization to the nucleus. Cells were immunostained with anti-HK2 (HK2; red). The nucleus is marked with DAPI (blue). Merged images (Merge) are shown. Representative images of 63× magnification from three independent experiments are shown for the indicated conditions. SP denotes JNK inhibitor (SP600125). Adjacent line profiles show mean fluorescence intensities of HK2 and DAPI measured by ZEN lite 2.3 software (scale bars, 10 μm). Error bars represent S.E. *, p < 0.05.