Fig. 5.
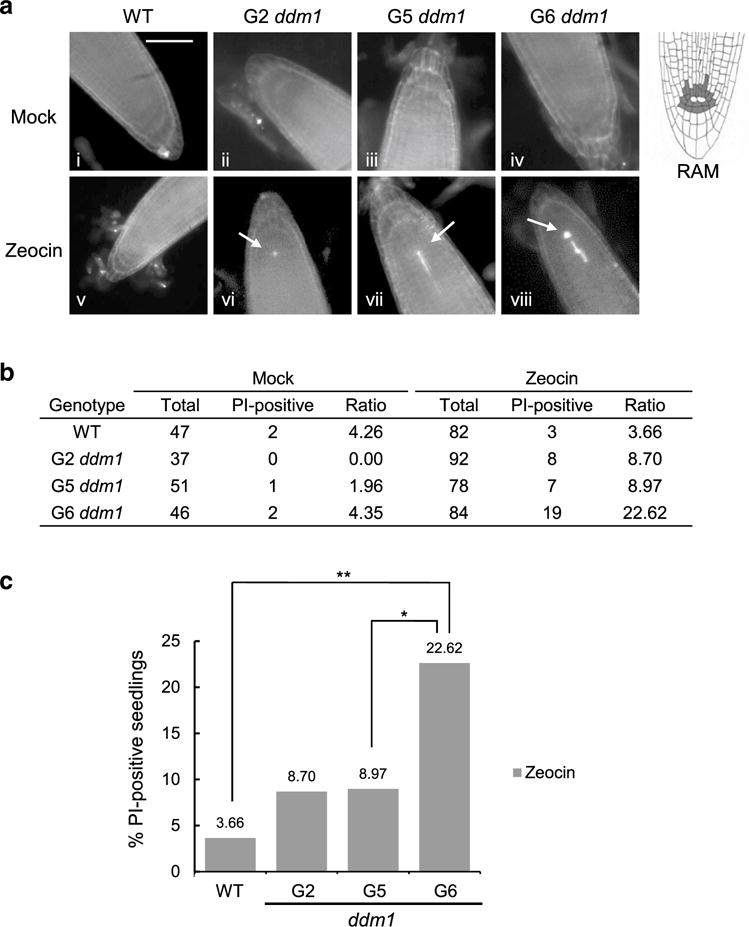
G6 ddm1-2 mutants are hypersensitive to DNA damage. a Representative images of root tips of 5-day-old WT and ddm1-2 mutant seedlings stained with propidium iodide (PI) to detect programmed cell death in the absence (i–iv) or presence (v–viii) of zeocin. Scale bar in a denotes 50 μm. Arrows denote PI-positive stem cells. For reference, a schematic diagram of the root tip is shown on the right. Dark gray cells in the root apical meristem (RAM) denote the stem and progenitor cells surrounding the quiescent center (in white). b Quantification of the percentage PI-positive RAM in WT and ddm1 mutants. c Graphic demonstration of the percentage of PI-positive RAM in the presence of zeocin. Single asterisk denotes p value < 0.05 (Fisher exact test) and double asterisks denote a p value < 0.005
