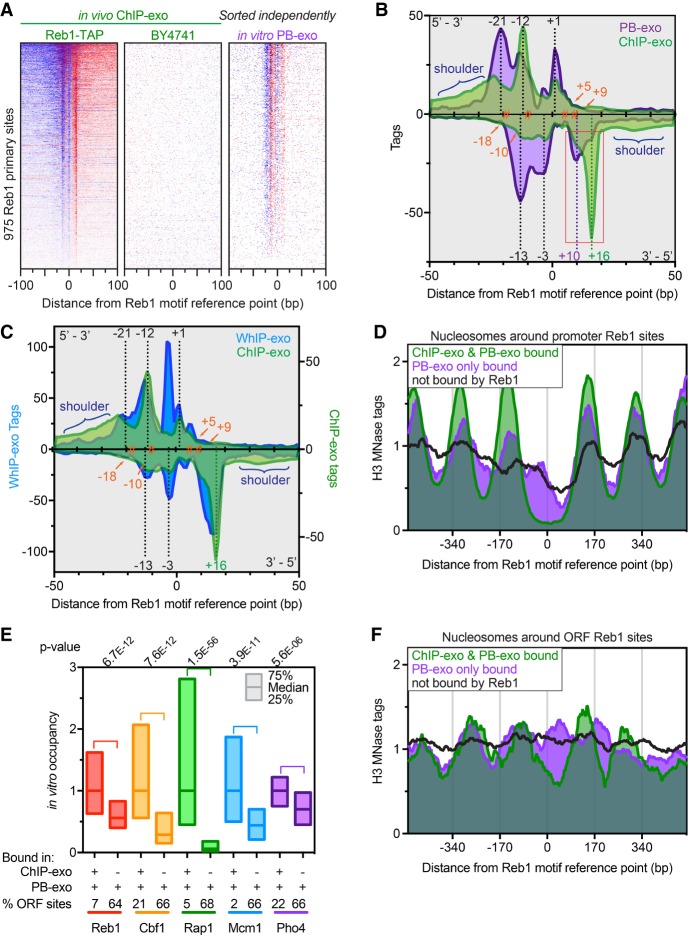
Figure 1.
Genome-wide in vitro binding of Reb1. (A) Heat maps comparing ChIP-exo and PB-exo at 975 TTACCCK Reb1 primary sites (rows) (Rhee and Pugh 2011). Distances are from the underlined motif reference point. ChIP-exo of strain BY4741 shows background, with rows linked to the Reb1 ChIP-exo sort. In vitro PB-exo was sorted independently. Blue indicates tag 5′ ends located on the same strand as the motif, whereas red are located on the opposite strand. (B) Composite of tag 5′ ends for ChIP-exo (green) and PB-exo (purple) of Reb1 at 975 primary sites. Density above the x-axis represents tags on the motif strand, whereas opposite strand density is inverted below the x-axis. The orange hashtags represent prominent cross-linking points calculated by pairing adjacent peaks above and below the x-axis. Dashed black lines represent peaks that are common in ChIP-exo and PB-exo. Dashed green and purple lines represent the peaks that are enriched in ChIP-exo and PB-exo, respectively, and are highlighted by the red box. The blue brackets highlight the “shoulder” regions that contain higher cross-linking in the ChIP-exo samples. (C) Composite of tag 5′ ends for ChIP-exo (green) and WhIP-exo (blue) of Reb1 at Reb1 primary sites. Annotation descriptions and the ChIP-exo trace are the same as in B. (D) Composite plots of nucleosome midpoints generated by MNase H3 ChIP-seq at different groups of Reb1 motif occurrences located in promoters. (E) Relative occupancy at sites detected in both ChIP-exo and PB-exo assays (+/+) versus sites detected only by PB-exo (−/+) and the percentage of those sites located in ORFs for all proteins in this study (except Abf1). Abf1 was excluded because its G/C cross-linking bias made for a potentially misleading comparison. The 25th, 50th, and 75th percentiles are marked. The proteins are arranged, left to right, by their propensity to cause nucleosome depletion (Kaplan et al. 2009). (F) Composite plots of nucleosome midpoints generated by MNase H3 ChIP-seq at different groups of Reb1 motif occurrences located in ORFs.