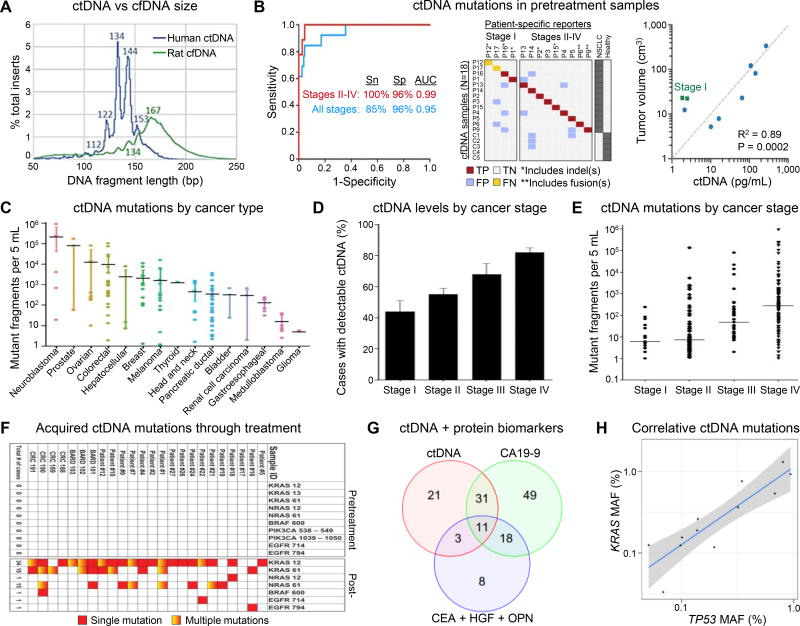
Figure 2. cfDNA and ctDNA analysis.
(A) Fragment sizes of ctDNA (human) and cfDNA (rat) in a GBM xenograft. Nearly identical cfDNA distributions were observed in healthy human plasma. Reproduced from15 with permission. (B) (left) Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis of plasma DNA samples from samples from all stages (n = 13 patients) and stages II–IV (n = 9 patients). Area Under the Curve (AUC) values are significant at P < 0.0001. Sn, sensitivity; Sp, specificity. (middle) Raw data related to left panel. TP, true positive; FP, false positive; TN, true negative; FN, false negative. (right) Concordance between tumor volume, measured by CT or PET/CT, and pg/mL of ctDNA from pretreatment samples (n = 9), measured by CAPP-Seq. Reproduced from35 with permission. (C) Quantification of mutant fragments in the plasma of patients with different cancers. Error bars represent the 95% bootstrapped confidence interval of the mean. (D) Fraction of patients with detectable ctDNA and (E) quantification of mutant fragments in cancer cases categorized by stage. Error bars represent the standard error in the measurement (SEM). (F) Heat map of acquired resistance mutations to EGFR blockade in ctDNA from patients with metastatic CRC. Panels C-F reproduced from46 with permission. (G) Combining ctDNA and protein markers increases sensitivity because a large proportion of patients are detected by only one marker. The Venn diagram shows the number of patients detected by ctDNA KRAS mutations (red circle), CA19-9 (green circle), the three other protein biomarkers (blue circle), and by combinations thereof (overlapping regions). Eighty patients (36% of the total) were not detected by any of the three makers. (H) MAF of KRAS and TP53 mutations are strongly correlated in the plasma of the 12 patients whose plasma contained detectable amounts of both mutations providing validation of the reliability of the ctDNA assay and its quantitative nature. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval. Panels G,H reproduced from49 with permission.