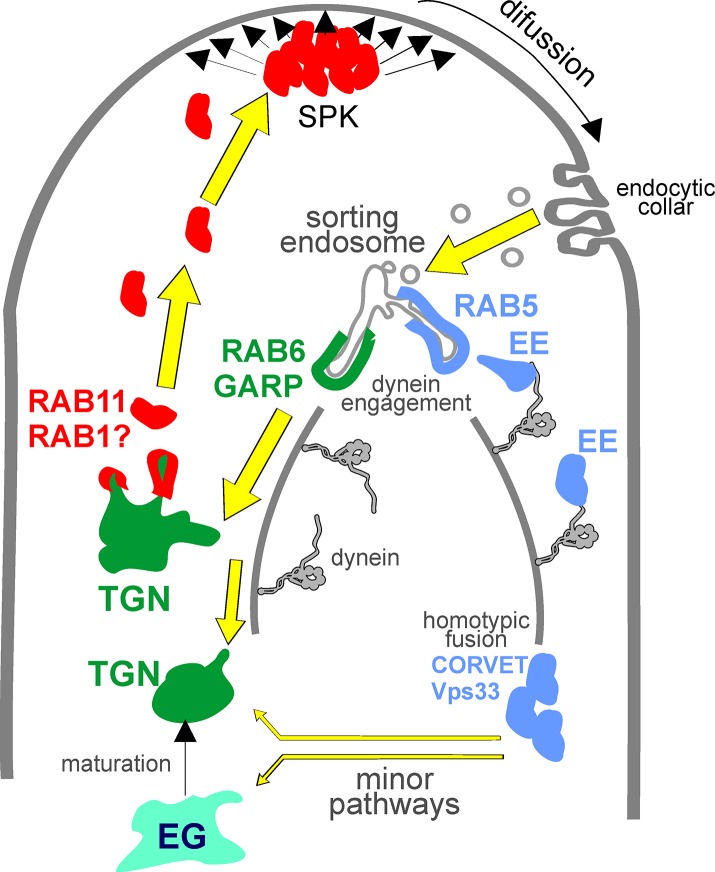
Fig 12. A model for ChsB recycling ChsB is transported with SVs (red) that accumulate at the SPK before being transported and tethered to the apical PM to undergo fusion.
Once inserted into the PM ChsB undergoes diffusion away from the apex until it is captured and endocytosed by the subapical endocytic collar. Endocytic vesicles containing ChsB reach a mosaic of sorting endosomes. Here domains enriched in RabBRAB5 acquire EE identity (blue), engage dynein by means of the Hook complex and undergo basipetal transport and maturation across the degradative endocytic pathway. ChsB segregates into ‘recycling’ domains (green) that are delivered to the TGN in a RabCRAB6-, GARP- and dynein-dependent manner. Once at the TGN ChsB is selected into RabERAB11 SVs (red), perhaps with cooperation of RabORAB1, and delivered to the SPK. Alternative minor pathways (thinner yellow arrows) between degradative endosomes and either the TGN or the early Golgi (EG) that ensure the robustness of this crucial circuitry must exist, accounting for the proportion of ChsB that persists in the apical dome in the absence of RabCRab6 /GARP.