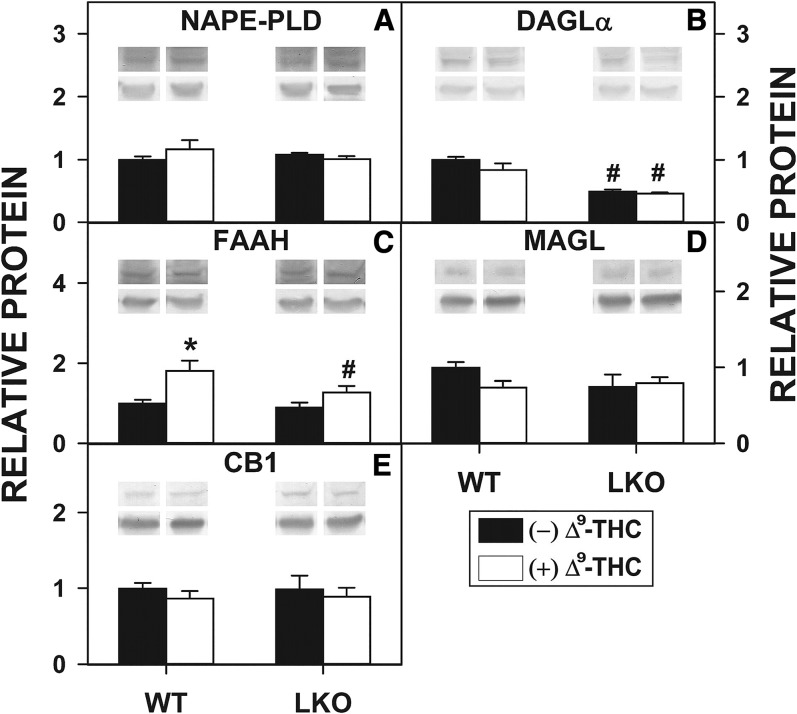
Fig. 6.
Effect of Δ9-THC and Fabp1 gene ablation on hepatocyte levels of proteins involved in EC synthesis, degradation, and action. Cultured primary hepatocytes were isolated from WT or LKO mice, plated on culture dishes, and incubated with Δ9-THC (20 μM) for 1 h, as described in the Materials and Methods. Hepatocytes were then washed, homogenized, protein determined, and aliquots used for SDS-PAGE and Western blotting [as we described (79, 87)] to determine levels of the following proteins: 46 kDa NAPE-PLD (A), 120 kDa DAGLα (B), 63 kDa FAAH (C), 33 kDa MAGL (D), and 53 kDa CB1 (E). The insets show representative Western blots of the respective protein (upper blot) and the gel-loading control protein (37 kDa GAPDH, lower blot). Relative protein was normalized to internal control and WT was set to 1. Values represent the mean ± SEM, n = 4–6. #P < 0.05 versus WT in the same treatment groups; *P < 0.05 versus untreated of the same genotype.