Figure 2.
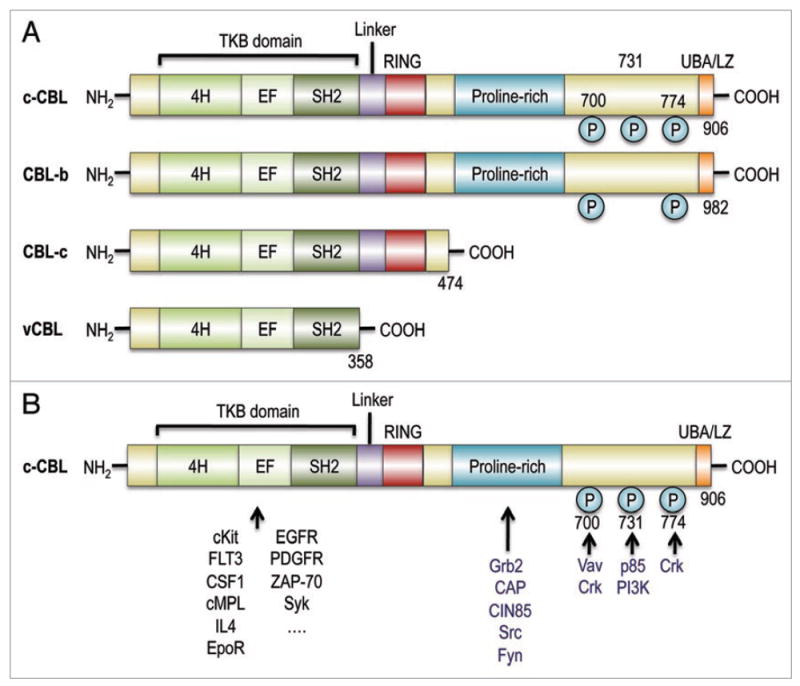
(A) Structure of CBL family proteins. CBL family proteins in mammals have highly conserved domains, where an N-terminal TKB domain, consisting of a four-helix bundle (4H), a Ca2+-binding EF (EF), and a src-homology (SH2) domains, is connected to a RING finger domain via a linker. c-CBL and CBL-b, but not CBL-c, have a proline-rich and other C-terminal components that end with a ubiquitin-associated and leucine zipper (UBA/LZ) domain. Their viral form, v-CBL, is truncated just after its SH2 domain. (B) CBL family proteins interact with a number of signal transducing molecules. Through their TKB domain, CBL family proteins target phosphrylated tyrosine kinases, including growth factor receptors and cytokine receptors, as well as, non-receptor tyrosine kinases. Ubiquitin conjugating enzymes have contact with CBL proteins via the linker/RING finger domain, which is central to the E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. The proline-rich domain provides a binding site for SH3 domains of Grab2, CAP and Src-family kinases. The C-terminal portion contains three tyrosine residues, Y700, Y731 and Y774, which are the major phosphorylated tyrosines, and which bind to the p85 subunit of PI3 kinase (Y731), Vav (Y700) and Crk proteins (Y700 and Y774).
