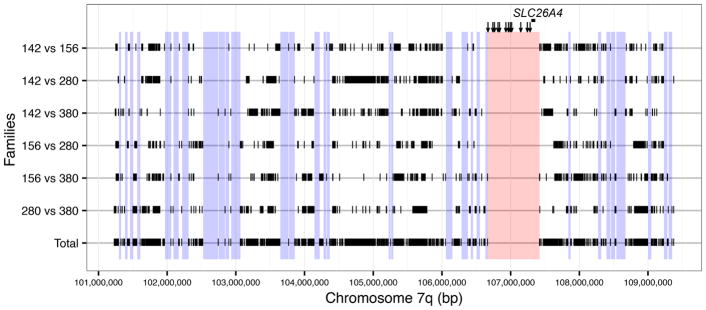
Figure 2.
Homozygosity haplotype analysis of alleles of SLC26A4 with no detectable mutations in the coding regions or splice sites in M1 families. Homozygous SNPs in the 8.218 Mb smallest region of overlap (figure 1A) were compared between pairs of chromosomes from four M1 families. Black vertical tick marks (|) show unmatched homozygous SNPs between each pair of chromosomes (ie, GG vs CC). Segments bounded by two tick marks indicate regions potentially shared by the two families. All unmatched pairwise homozygous SNPs from the six comparisons are shown at the bottom (‘Total’), delineating intervening regions that may be shared among the four chromosomes from the four families. The longest segment (shown in red) includes the Caucasian enlarged vestibular aqueduct haplotype markers (vertical arrows) and SLC26A4. Other segments longer than 35 kb (shown in blue) were analysed by massively parallel sequencing.