Fig. 1.
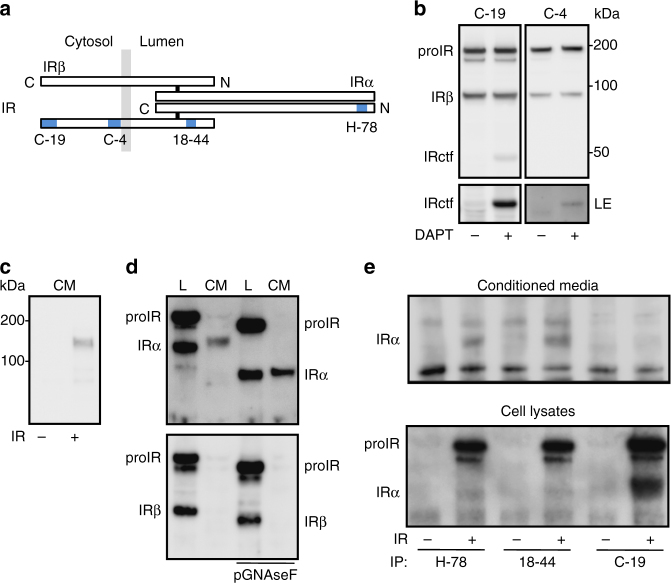
Detection and characterization of IR fragments. a Schematic representation of IR showing the position of the peptides used as antigens to produce antibodies C-19, C-4, H-78, and that of the epitope recognized by antibody 18-44 (blue rectangles). N and C-terminal extremities and α and β subunits are localized. The membrane is represented by the light gray rectangles. b HEK 293 cells were transfected with IR expression vector and treated overnight with the γ-secretase inhibitor (DAPT; 5 μM). IR was detected by immunoblot, using the indicated IR β-subunit (IRβ) specific antibodies (LE indicates a long exposure of the immunoblot). Positions of IR precursor (proIR), IRβ, and C-terminal fragment of IR (IRctf) are indicated. c Immunoblot analysis using the H-78 antibody of 24 h serum-free conditioned media (CM) from cells transfected with an empty plasmid (−) or with a plasmid encoding human IR (+). d Lysates (L) and CM from IR overexpressing cells were collected and where indicated in vitro, deglycosylated by PGNaseF. IR was detected by immunoblot, using H-78 antibody (upper panel) or C-19 antibody (lower panel). e CM and cell lysates from IR overexpressing cells (+) or cells transfected with an empty plasmid (−) were collected and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP), using the indicated antibodies. IR was detected by immunoblot using H-78 antibody. IRα indicates the position of IR α-subunit