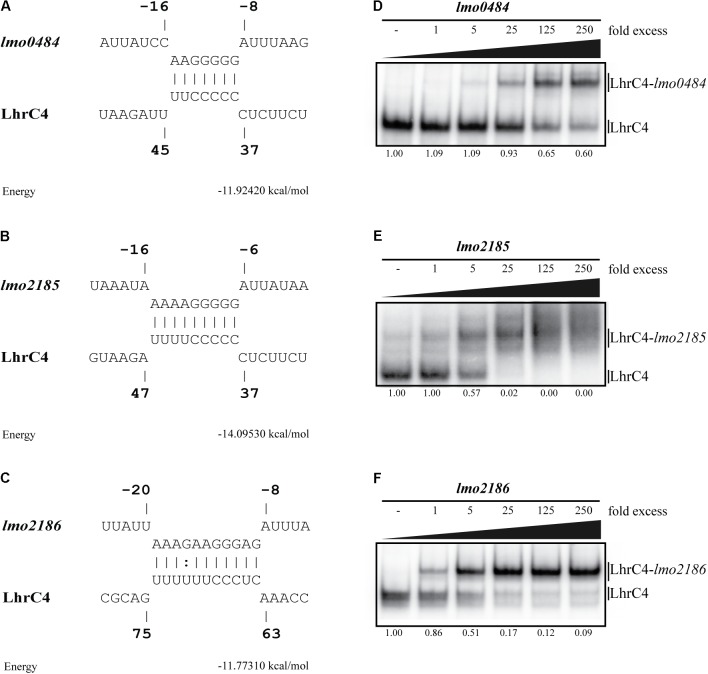
FIGURE 4.
Analyzing the sRNA-mRNA interaction between LhrC4 and lmo0484, lmo2185, or lmo2186. (A–C) In silico prediction of sRNA-mRNA interactions. According to the IntaRNA Software (Busch et al., 2008; Wright et al., 2014; Mann et al., 2017), the loop A of LhrC4 binds to (A) lmo0484 and (B) lmo2185 mRNAs, and the single-stranded stretch binds to (C) lmo2186 mRNA. All the interactions are predicted to block the SD sequence of the mRNAs. LhrC4 is shown as a representative of the five LhrC copies. The nucleotides of lmo0484, lmo2185, and lmo2186 are numbered relative to the translation start site, and the nucleotides of LhrC4 are numbered relative to the 5′-end of the sRNA. (D–F) Testing the formation of sRNA-mRNA complexes by EMSAs. Labeled LhrC4 was shifted with increasing concentrations of unlabeled (D) lmo0484 RNA, (E) lmo2185 RNA or (F) lmo2186 RNA. Fold excess refers to the amount of unlabeled mRNA added to each sample, relative to the amount of labeled LhrC4. The fraction of unbound LhrC4 is shown below each lane.