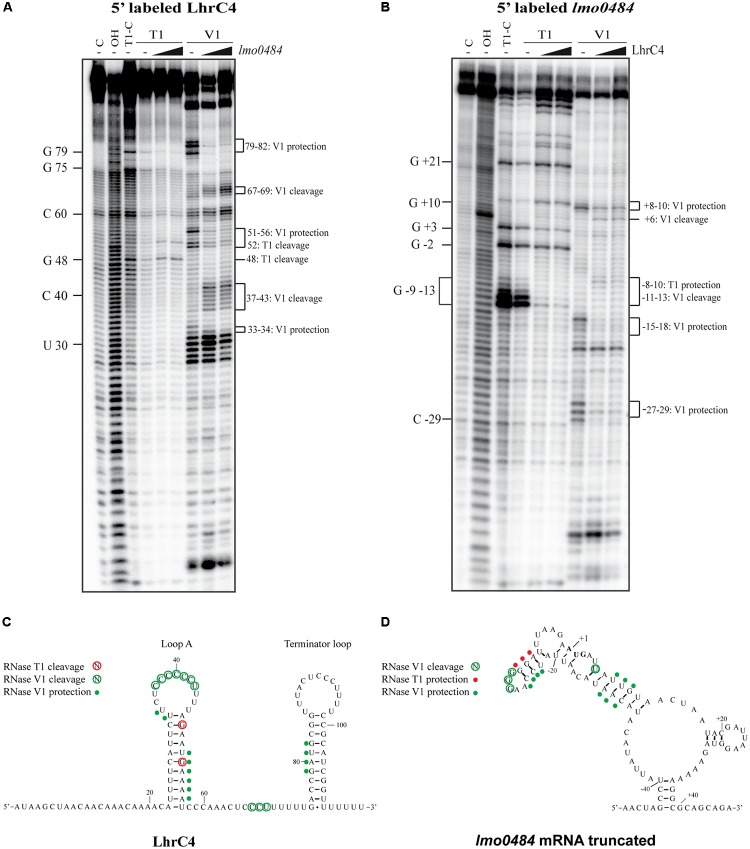
FIGURE 6.
Structure probing of LhrC4 and lmo0484 mRNA interaction. (A) 5′-end labeled LhrC4 was treated with RNase T1 or RNase V1, either in the absence (–) or in the presence of 25- or 250-fold excess of unlabeled lmo0484 RNA. As a control, untreated LhrC4 was separated in the first lane (C), an alkaline ladder (OH) is shown in the second lane and an RNase T1 ladder (T1-C) was separated in the third lane. For an overview, selected nucleotides are labeled on the left side. Nucleotides showing structural changes upon lmo0484 binding are marked on the right side of the gel. (B) Partial digestion of 5′-end labeled lmo0484 RNA with RNases T1 and V1. Untreated lmo0484 RNA (C), an alkaline ladder (OH) and an RNase T1 ladder (T1-C) are shown in the first three lanes. Some of the cleaved G residues are labeled along the left side of the gel. The lmo0484 nucleotides, that were protected or cleaved in the presence of LhrC4, are indicated on the right side of the gel. (C) Secondary structure of LhrC4 illustrating the cleavage pattern upon binding to lmo0484 mRNA. Residues cleaved by RNase T1 (red) or RNase V1 (green) are encircled. Residues of LhrC4, that appeared to be protected by lmo0484 RNA, are indicated by green dots. The nucleotides of LhrC4 are numbered relative to the 5′-end of the sRNA. (D) Secondary structure of the truncated version of lmo0484 mRNA showing an altered cleavage pattern upon the addition of LhrC4. Residues cleaved by RNase V1 (green) are encircled. Residues of lmo0484 RNA that were protected in the presence of LhrC4 are indicated by red dots (T1 protection) or green dots (V1 protection). The start codon is indicated in bold. The nucleotides of lmo0484 are numbered relative to the translation start site (+1).