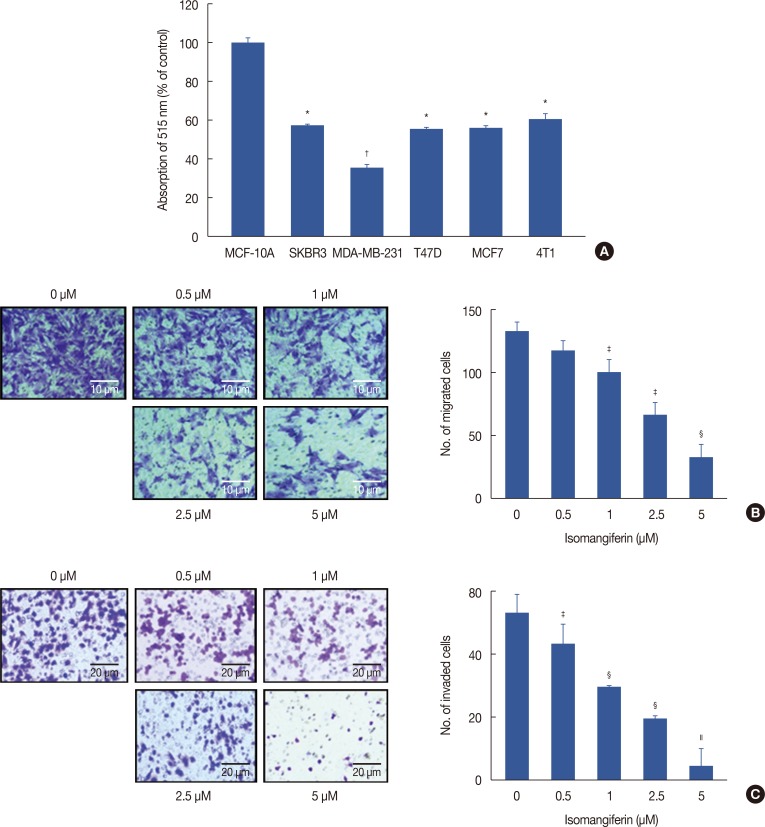
Figure 2. Isomangiferin inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion. (A) Isomangiferin inhibited different types of breast cancer cells proliferation. Five variable kinds of breast cancer cells and one normal breast cell MCF-10A were treated with different doses of isomangiferin for 48 hours. Data are shown as mean±standard error of the mean (SEM) from triplicate experiments. The cell viability was determined by MTS assay according to Methods. (B) Isomangiferin supressed MDA-MB-231 migration. MDA-MB-231 cells were seeded in transwell chambers and then deprived of fetal bovine serum (FBS) for 6 hours. After that, cells were treated with 10 ng/mL vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and indicated concentrations of isomangiferin. The migrated cells were quantified by manual counting by using an microscope (scale bar, 10 µm). Values are shown as mean±SEM of three independent experiments. (C) Isomangiferin imparied MDA-MB-231 invasion. After MDA-MB-231 cells seeded in the upper chamber of a transwell which has been pre-coated with Matrigel, the cells were deprived of FBS and then treated with different concentrations of isomangiferin. After 8 to 10 hours, the MDA-MB-231 cells that invaded through the membrane from the upper chamber to the bottom chamber were quantified when stimulated by the bottom chamber which was added VEGF (scale bar, 20 µm). Values are shown as mean±SEM of three independent experiments.
*p<0.05 vs. MCF-10A; †p<0.01 vs. MCF-10A; ‡p<0.05 vs. 0 µM isomangiferin; §p<0.01 vs. 0 µM isomangiferin; ∥p<0.001 vs. 0 µM isomangiferin.