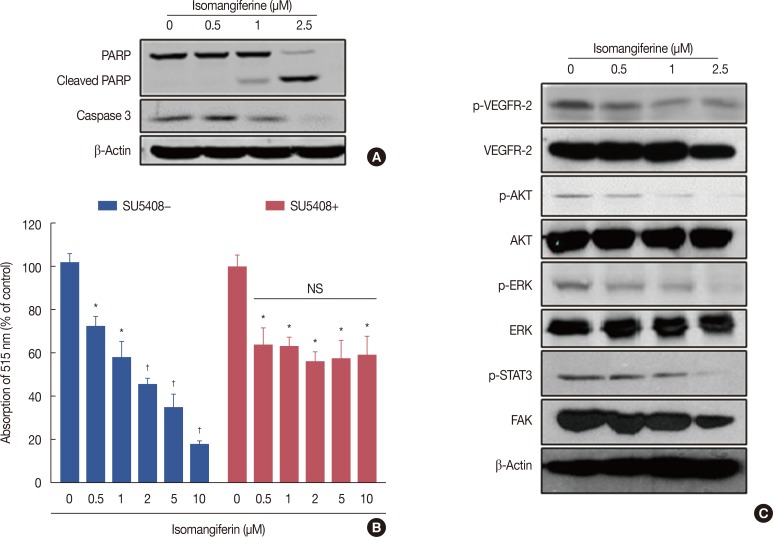
Figure 4. Isomangiferin suppresses breast cancer through inhibiting the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) signaling pathway. (A) Isomangiferin induced cell apoptosis. Proteins from MDA-MB-231 cells treated with indicated concentrations of isomangiferin for 24 hours were submitted to Western blot for the immunoblotting of caspase-3 and cleaved poly ADP-ribose polymerase (cleaved PARP). (B) Isomangiferin's ihibiton on breast cancer cell proliferation was dependent on VEGFR-2 activity. 100 nM SU5408 was used or not to block VEGFR-2's activity and then MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with isomangiferin. The cell proliferation was assessed by MTS assay. Values are shown as mean±standard error of the mean of three independent experiments. (C) Isomangiferin suppressed the activation of VEGFR-2 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). The activation of VEGFR-2 was analyzed by Western blot and probed with indicated antibodies. Western blot was conducted in the way that described in Methods and specific antibodies were used accordingly.
PARP=poly ADP-ribose polymerase; NS=not significant; p-AKT=phosphorylated protein kinase B, p-PKB/p-AKT; AKT=protein kinase B, PKB/AKT; p-ERK=phosphorylated extracellular regulated protein kinases; ERK=extracellular regulated protein kinases; p-STAT3=phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; FAK=focal adhesion kinase. *p<0.05 vs. control; †p<0.01 vs. control.