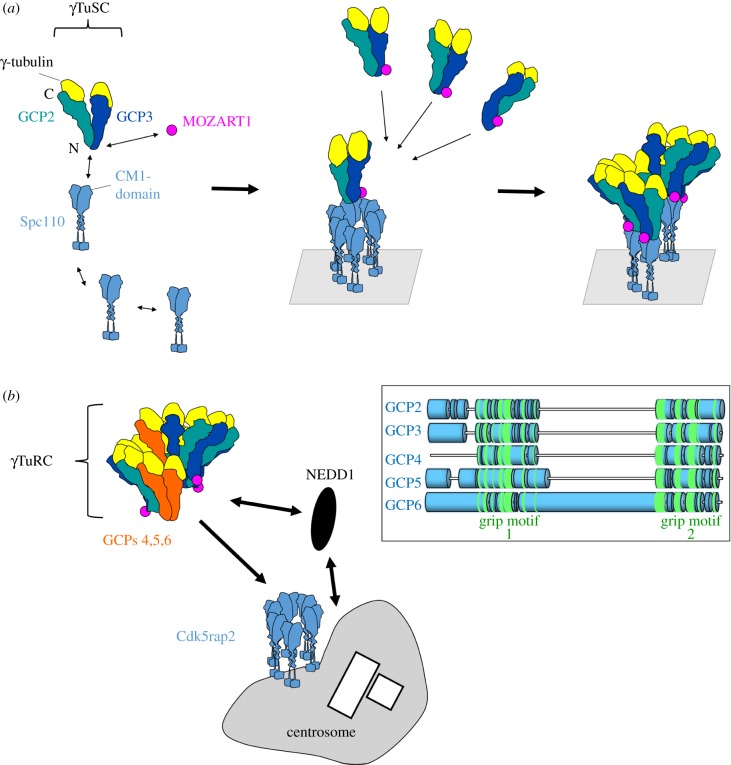
Figure 1.
Assembly and recruitment of γ-tubulin complexes. (a) GCP2 and GCP3 interact laterally, and bind longitudinally each to one molecule of γ-tubulin, to form the γTuSC. Assembly of helical complexes from γTuSCs is driven by oligomerization of proteins with a CM1 domain, such as Spc110 in S. cerevisiae. The CM1 domain binds to the amino-terminal region of GCP3, together with a small oligomerization-promoting protein, MOZART1. (b) Soluble γTuRCs are fully assembled in the cytoplasm, and are recruited to the centrosome by NEDD1 and by CM1 proteins, such as Cdk5rap2 in mammals. The inset depicts schematically sequence similarities between GCPs 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. Conserved secondary structures are found in the amino-terminal grip1 domain, and in the carboxy-terminal grip2 domain (highlighted in green). GCPs 5 and 6 contain unique sequence extensions at their extreme amino-termini and between the grip1 and grip2 domains that are not shared with any other GCPs.