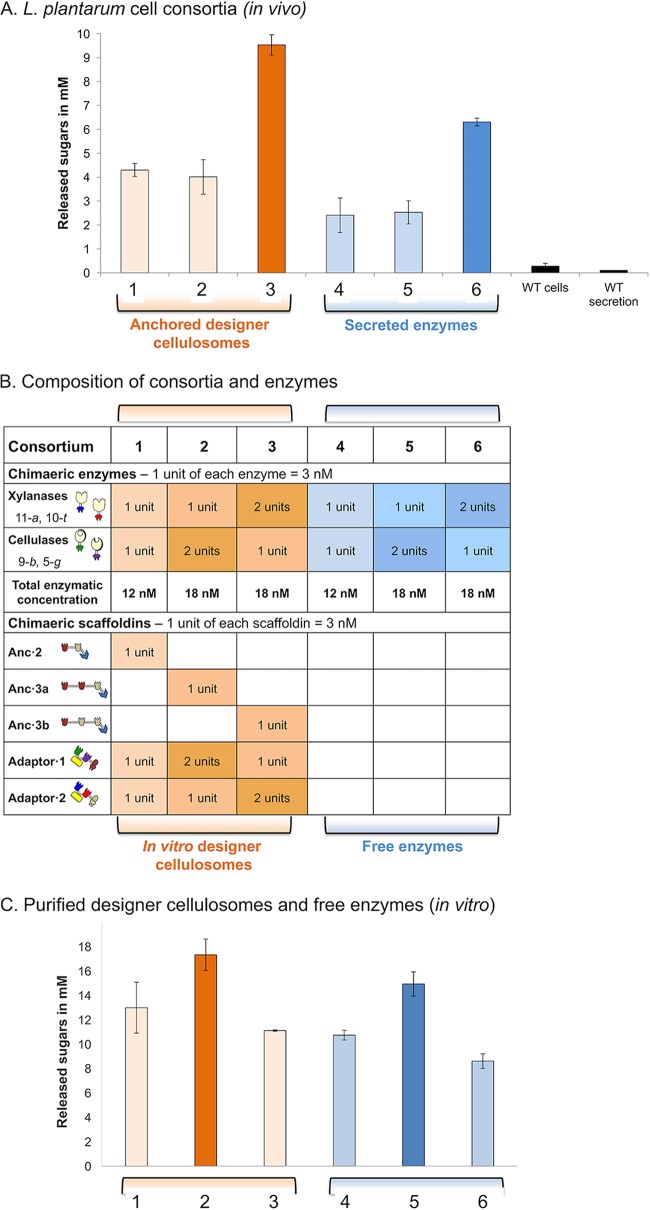
FIG 3.
Comparative analysis of hydrolysis of hypochlorite-pretreated wheat straw by free enzymes versus cell-associated and cell-free designer cellullosomes. (A) Soluble sugars produced in the extracellular medium by different transformed L. plantarum consortia versus the wild-type (WT) strain. Reaction mixtures were incubated for 96 h at 37°C. For consortia 1, 2, and 3 and for WT cells, washed cells were used in the enzymatic reaction, whereas for consortia 4, 5, and 6 and for WT secretion cells, concentrated supernatant fluids were used. Hypochlorite-pretreated wheat straw was used at a concentration of 40 g/liter, and enzymatic activities are represented by the concentrations of total reducing sugars (expressed in millimoles). Experiments were conducted three times with triplicate samples, and standard deviations are indicated. (B) The recombinant enzymes and chimeric scaffoldins that were introduced in the different L. plantarum consortia are indicated and correspond to the respective bars in the chart. The molar ratios between the proteins, the numbers of units, and total enzyme concentrations are stipulated. (C) Soluble sugars produced by recombinant cell-free designer cellulosome assemblies and free enzyme mixtures parallel to the ones used as described for panel A and assembled from purified proteins produced by E. coli. The cellulosomal components were assembled stoichiometrically, where the concentration of the anchoring scaffoldin was set at 12 nM. The designer cellulosomes were allowed to assemble for 3 h at room temperature with all components of the enzymatic assay except the wheat straw substrate. The enzymatic reaction mixture was incubated for 96 h at 37°C under shaking conditions. Experiments were conducted three times with triplicate samples, and standard deviations are indicated.