Figure 2.
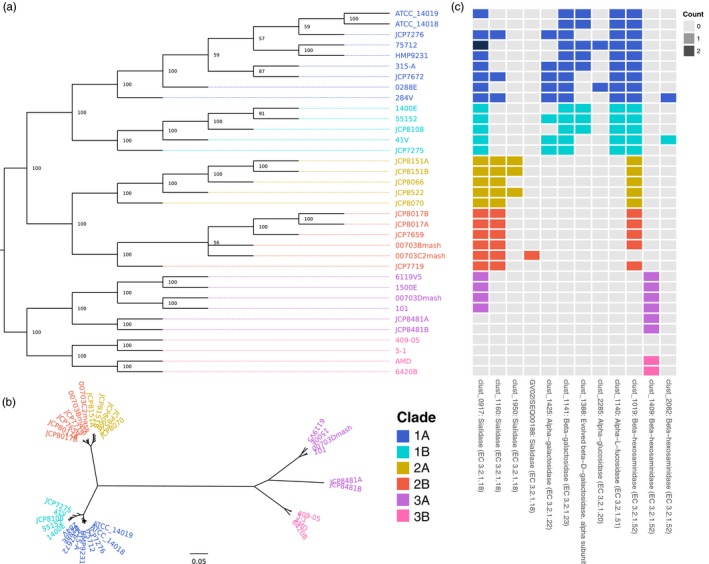
Majority‐rule consensus tree estimated on the concatenated sequence of the core genome (664 single‐copy genes) and the presence/absence data of accessory genes. (a) Unscaled tree; branch labels indicate bootstrap support (as percentage of gene trees that contain a bipartition). Tips are labeled with the G. vaginalis strain identifiers and colored according to putative taxonomic clades. (b) Majority‐rule consensus tree with topology fixed as shown in (a) with branch lengths scaled by the average core gene distances. (c) Counts of select protein families with putative mucus degradation capability that were differentially enriched among clades of G. vaginalis. The most prevalent annotation among each protein family is listed to along with the OrthoMCL cluster identifier. The clade color scheme in (b) applies to all panels of the figure
