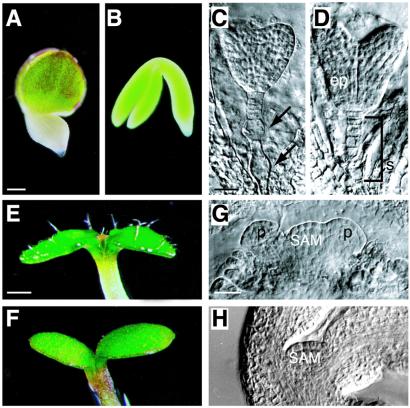
Figure 1.
Morphological phenotype of lec2 mutants. (A) lec2-5, (C) lec2-3, and (E, G) lec2-4 mutant embryos. (B, D, F, H) Wild-type embryo. (A and B) Whole-mount photographs of maturing embryos. (C and D) Embryonic suspensors as viewed by using differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy of cleared seeds. Arrows point to abnormal suspensor cells in lec2 mutants. (E and F) Cotyledons of seedlings grown for 4–5 days. A lec2 mutant seedling germinated before desiccation possessed trichomes on the adaxial surface of cotyledons. (G and H) Shoot apices of curled cotyledon-stage embryos seen with DIC optics. The shoot apical meristem of lec2 mutants is domed and possesses leaf primordia in contrast to the unactivated meristem of wild types. ep, Embryo proper; p, leaf primordium; SAM, shoot apical meristem; s, suspensor. [Bars = 100 μm (A), 20 μm (C, G), 300 μm (E).]