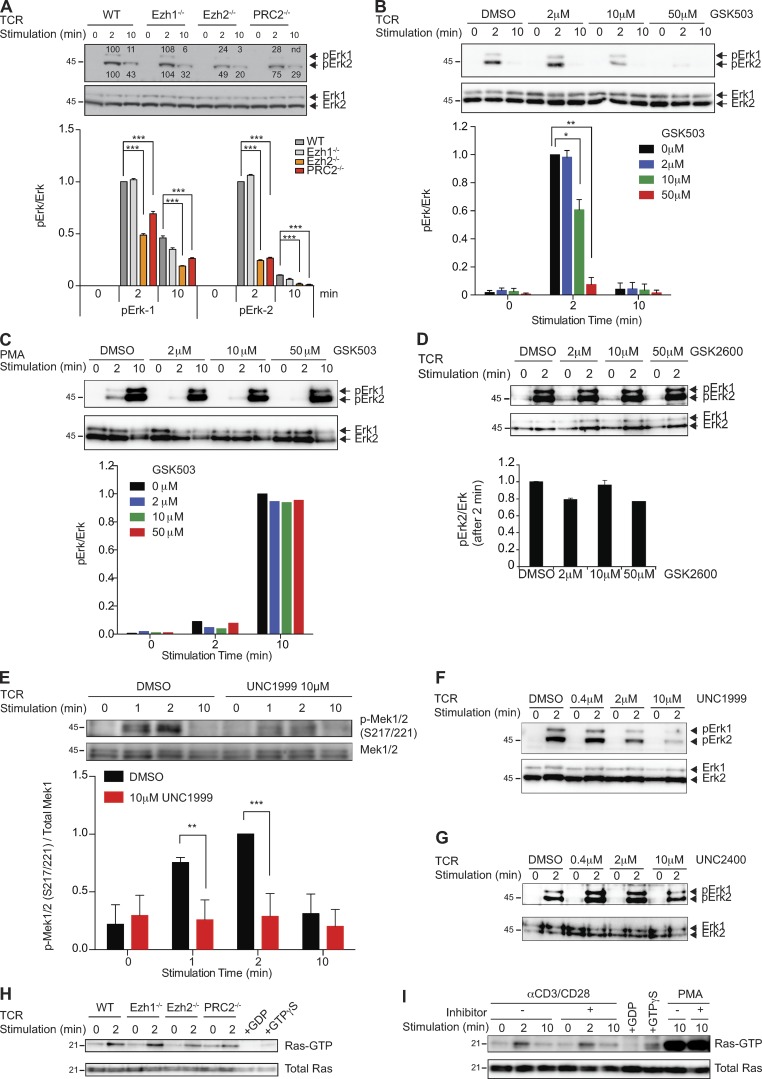
Figure 4.
PRC2 regulates TCR-mediated Mek-Erk1/2 phosphorylation. (A) Phosphorylation of Erk1/2 (pErk1/2) in naive and TCR-triggered WT and indicated mutant CD4+ T cells were measured and normalized to the total amount of Erk1/2. Cells were stimulated by a combination of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies for the indicated time periods. The bar graph shows the quantification of these measurements. Results from one of three independent experiments are shown. (B and C) Phosphorylation of Erk1/2 (pErk1/2) in naive and TCR-triggered WT CD4+ T cells in the absence (DMSO) or presence of the indicated amounts of the Ezh2 inhibitor GSK503 was measured and normalized to the total amount of Erk1/2. Cells were stimulated by a combination of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies (B) or PMA (C) for the indicated time periods. The bar graphs show the quantification of these measurements. Results from one of three independent experiments are shown. (D) Phosphorylation of Erk1/2 (pErk1/2) in naive and TCR-triggered WT CD4+ T cells in the absence (DMSO) or presence of the indicated amounts of the control compound GSK2792600 (GSK2600) was measured and normalized to the total amount of Erk1/2. Cells were stimulated by a combination of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies for the indicated time periods. The bar graph shows the quantification of these measurements. Results from one of three independent experiments are shown. (E) WT CD4+ T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies in the absence (DMSO) or presence of 10 µM UNC1999. The levels of pMek1/2 (S217/221) were measured and normalized to the total amount of Mek1. The bar graph shows the quantification of these measurements. Results from one of three independent experiments are shown. (F) Phosphorylation of Erk1/2 (pErk1/2) in naive and TCR-triggered WT CD4+ T cells in the absence (DMSO) or presence of the indicated amounts of the Ezh2 inhibitor UNC1999 was measured and normalized to the total amount of Erk1/2. Cells were stimulated by a combination of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies for the indicated time periods. Results from one of three independent experiments are shown. (G) Phosphorylation of Erk1/2 (pErk1/2) in naive and TCR-triggered WT CD4+ T cells in the absence (DMSO) or presence of the indicated amounts of control compound UNC2400 was measured and normalized to the total amount of Erk1/2. Cells were stimulated by a combination of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies for the indicated time periods. The experiments were performed independently three times, and significance, when calculated, was determined by the unpaired Student’s t test: *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; and ***, P ≤ 0.001. (H) GTP-bound Ras in naive and TCR-stimulated WT and indicated mutant CD4+ T cells was detected by Raf1-RBD pulldown assay. (I) WT CD4+ T cells were treated with 10 µM UNC1999 or DMSO and stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies. Ras-GTP pulldown assay was performed. Data from one representative of two independent experiments are shown for H and I. Molecular mass is indicated in kilodaltons. Error bars show mean ± SEM.