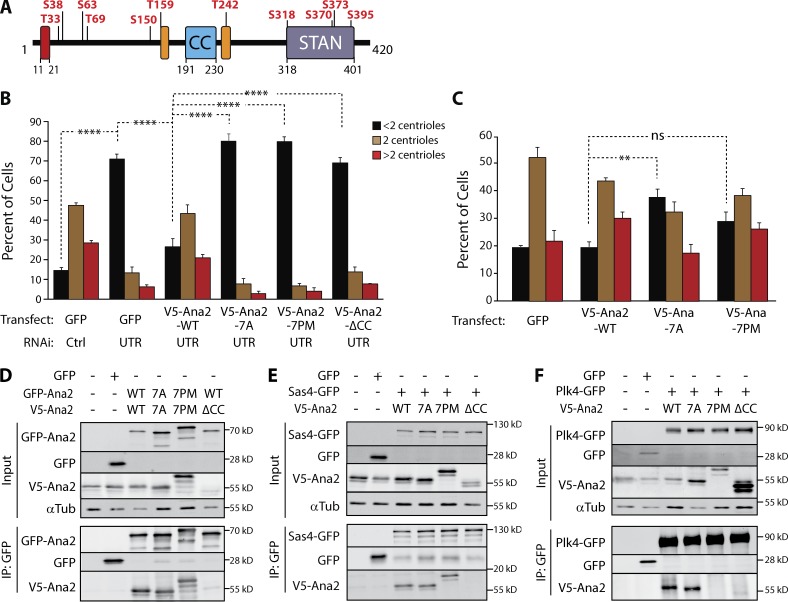
Figure 2.
Ana2 is a Plk4 substrate; expression of phospho-Ana2 mutants inhibits centriole duplication. (A) Linear map of Ana2 depicting the Plk4 phosphorylation sites. Phospho-sites were identified by tandem MS of purified GST-Ana2 phosphorylated in vitro by purified Plk4 1–317-His6. Red box, Sas4-binding site (Cottee et al., 2013); orange boxes, LC8-binding sites (Slevin et al., 2014). (B) NT phosphorylation mutations in Ana2 disrupt centriole duplication. On days 0, 4, and 8, S2 cells were treated with control dsRNA or depleted of endogenous Ana2 by RNAi (UTR). On days 4 and 8, cells were transfected with the indicated V5-Ana2 or GFP construct and then induced to express with 0.1 mM CuSO4. Cells were immunostained for PLP and Asterless to mark centrioles, and the number of centrioles per cell was counted. n = 100 cells in each of three experiments. Asterisks indicate significant differences: **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant. Error bars, SEM. (C) Expression of nonphosphorylatable Ana2-7A acts as a dominant/negative and inhibits centriole amplification. V5-Ana2 or GFP expression constructs were transfected on days 0 and 4 and induced with 0.5 mM CuSO4. Cells were fixed and immunostained on day 7. The mean percentages of cells containing the indicated number of centrioles are shown (n = 100 cells in each of three experiments). Error bars, SEM. Asterisks indicate significant difference: **, P < 0.01; ns, not significant. (D–F) The phosphorylation state of the Ana2 NT does not affect Ana2 binding to itself (D) or Sas4 (E). However, PM mutations in Ana2 (7PM) inhibit Plk4 binding, whereas Plk4 binding is not affected with nonphosphorylatable Ana2 (7A; F). In contrast, the CC of Ana2 is required for Ana2 self-association (D) and binding to Sas4 and Plk4 (E and F). S2 cells were depleted of endogenous Ana2 by RNAi for 7 d. On day 5, cells were cotransfected with the indicated constructs and the next day induced to express for 24 h. Anti-GFP IPs were then prepared from lysates, and Western blots of the inputs and IPs were probed for GFP, V5, and α-tubulin.