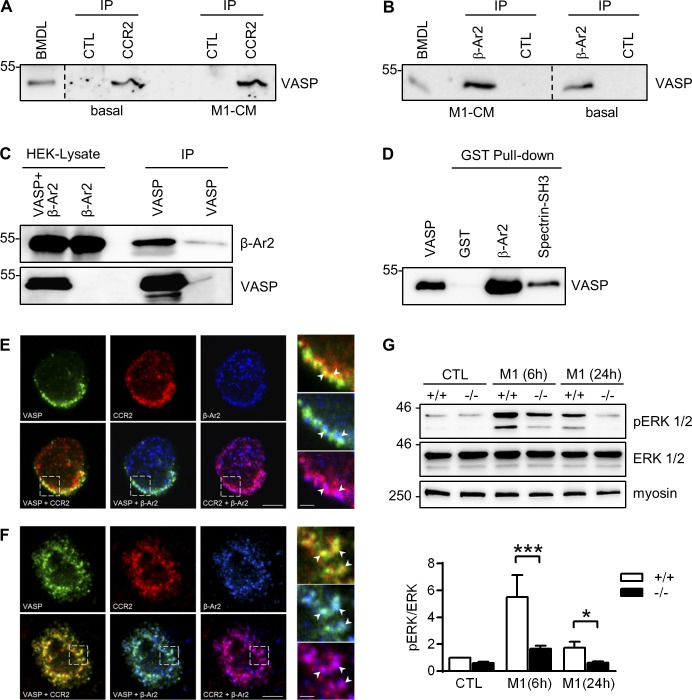
Figure 9.
VASP forms complexes with CCR2 and β-arrestin 2 in leukocytes. (A and B) Immunoprecipitation (IP) of VASP from BM-derived leukocytes under basal conditions and after incubated with M1 conditioned medium (M1-CM) using antibodies directed against CCR2 (A) or β-arrestin 2 (β-Ar2, B). A and B show different regions of the same blot; separations are indicated. (C) HEK cells were transfected with β-Ar2 with or without VASP. After IP of VASP, the precipitated material was probed with β-Ar2 antibodies. (D) Purified recombinant VASP was pulled down with GST (negative control), GST-β-Ar2, or GST-Spectrin-SH3 (positive control), and the precipitated material was probed with VASP-specific antibodies. (E and F) Colocalization of VASP (green) with CCR2 (red) and β-arrestin 2 (blue) in BM-derived monocytes under basal conditions (E) and after stimulation with mouse CCL2 (150 nmol/liter; F). Bars, 4 µm. The panels on the right are higher magnifications of the areas marked by the boxes. Bars, 1 µm. Comparable results of A–E were obtained in four additional experiments. (G) Analysis of ERK (also termed p42/p44 MAPK) phosphorylation in WT (+/+) and VASP−/− (−/−) CTL macrophages and macrophages after 6 or 24 h of M1 polarization (10 ng/ml LPS and 1 ng/ml IFNγ). Myosin served as loading control. n = 8 animals per group; error bars, SEM; *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001 (two-way ANOVA/Bonferroni).