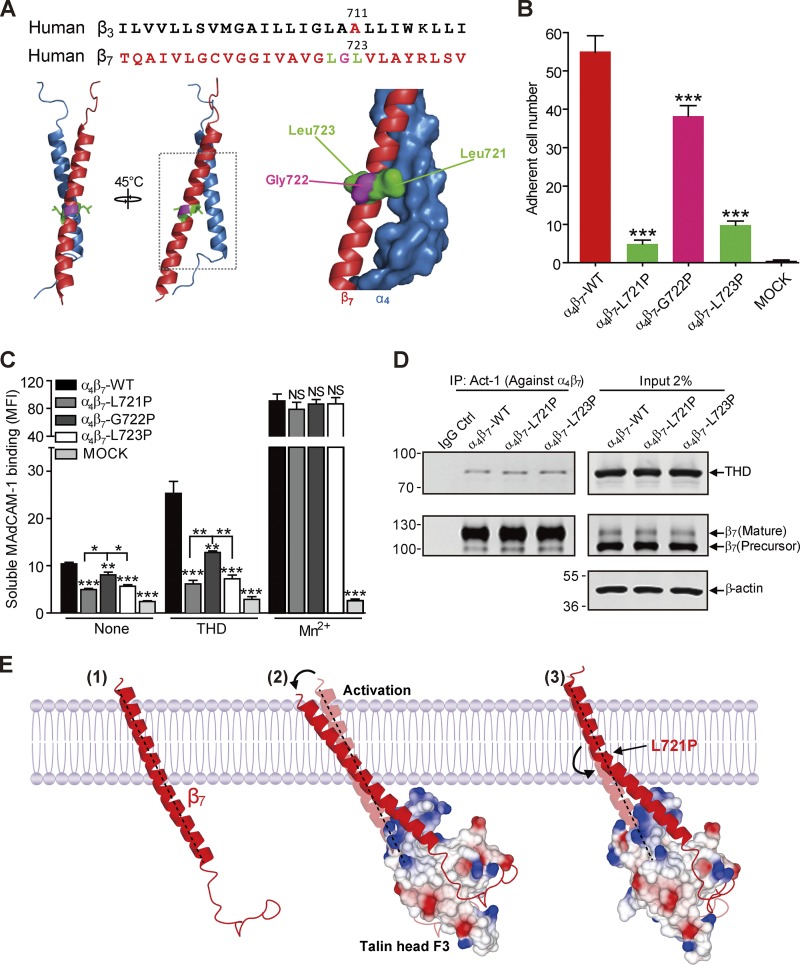
Figure 2.
Blocking talin-induced change in β7 TMD topology abolished α4β7 activation. (A) Sequence alignment of partial TMDs of integrin β3 and β7 subunits. β3 Pro mutant site Ala711 is highlighted in red. The sites in β7 that were mutated to Pro (Leu721 and Leu723) are highlighted in green and Gly722 is highlighted in pink and are projected onto a homology model of the α4β7 TMD (α4 in blue and β7 in red). (B) Adhesion of 293T cells transfected with β7 WT or mutations (L721P, G722P, or L723P) plus α4 on MAdCAM-1 under a wall shear stress of 2 dyn/cm2. Nontransfected 293T cells (MOCK) were used as a negative control (Ctrl). Mutant integrins were compared with the WT using one-way ANOVA. (C) Binding of soluble MAdCAM-1 to 293T cells transfected with WT α4β7 or α4 in combination with mutants (L721P, G722P, and L723P) in the presence or absence of THD. Nontransfected 293T cells (MOCK) were used as a negative control. Mutant integrins were compared with the WT for each condition using one-way ANOVA. Error bars show means ± SD. n = 5 (A and B) or 4 (C). *, 0.01 < P < 0.05; **, 0.001 < P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. (D) Coimmunoprecipitation of THD with α4β7 WT or mutants. Lysates of 293T cells were transfected as in C, in combination with THD-GFP, and α4β7 was isolated by immunoprecipitation (IP). Precipitated proteins were analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies and confirmed similar THD association with the mutant and WT integrins. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. Note that a shorter exposure time was used for the THD input. Molecular masses are given in kilodaltons. (E) A model of how a Pro mutation can prevent transmission of altered topology of the β7 TMD by talin. The complex formed between the β7 cytoplasmic tail/TMD (red) and cytoplasmic talin F3 domain (surface representation; colored by charge) alters the topology of the inner portion of the transmembrane helix, which is transmitted to the outer moiety, where it can disrupt the outer membrane clasp (Lau et al., 2009), resulting in destabilization of the α-β TMD complex and integrin activation. β7(L721P) breaks the TMD helix into two helices connected by a flexible kink; the flexible kink prevents transmission of the talin-induced change in intracellular TMD topology to stabilize the α-β TMD interaction and block talin-induced activation of integrin α4β7.