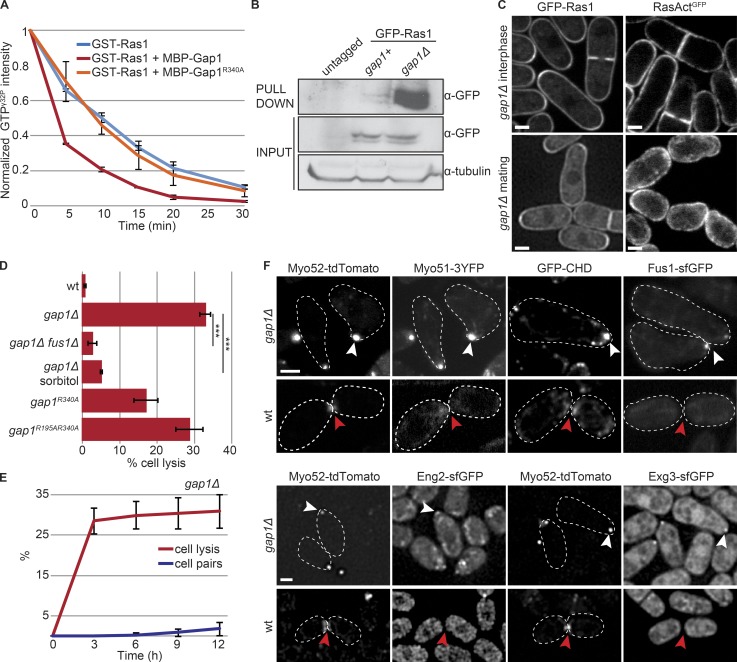
Figure 4.
Gap1 is a GTPase Activating Protein for Ras1. (A) In vitro GAP assays: MBP-Gap1, but not catalytically inactive MBP-Gap1R340A, increases the rate of GST-Ras1-GTPγ32P hydrolysis; n = 3. (B) GSTRBD pulldown of extracts from h-cells of indicated genotypes. (C) GFP-Ras1 (left) and RasActGFP (right) in gap1Δ strains during vegetative growth (top) and mating (bottom). Arrowheads indicate shmoo tips. (D) Percentage of cell lysis of h90 WT and gap1 mutant (gap1R340A, gap1R195A R340A, and gap1Δ) cells treated with 1.2 M sorbitol or lacking fus1 after 14 h in MSL-N (n > 500 for three independent experiments); ***, 9.34 × 10−7 ≤ P ≤ 6.54 × 10−6. (E) Time course of cell lysis and cell pair formation in h90 gap1Δ cells placed in MSL-N (n > 200 for three independent experiments). (F) Type V myosins (Myo52-tdTomato and Myo51-3YFP), actin (GFP-CHD), formin Fus1-sfGFP, and cell wall glucanases (Eng2-sfGFP and Exg3-sfGFP) are focalized in unpaired gap1Δ cells (white arrowheads) but either not detectable or not focalized (red arrowheads) in WT cells not yet engaged in fusion (early paired cells shown). Bars, 2 µm. Plots show means and SDs.