-
A
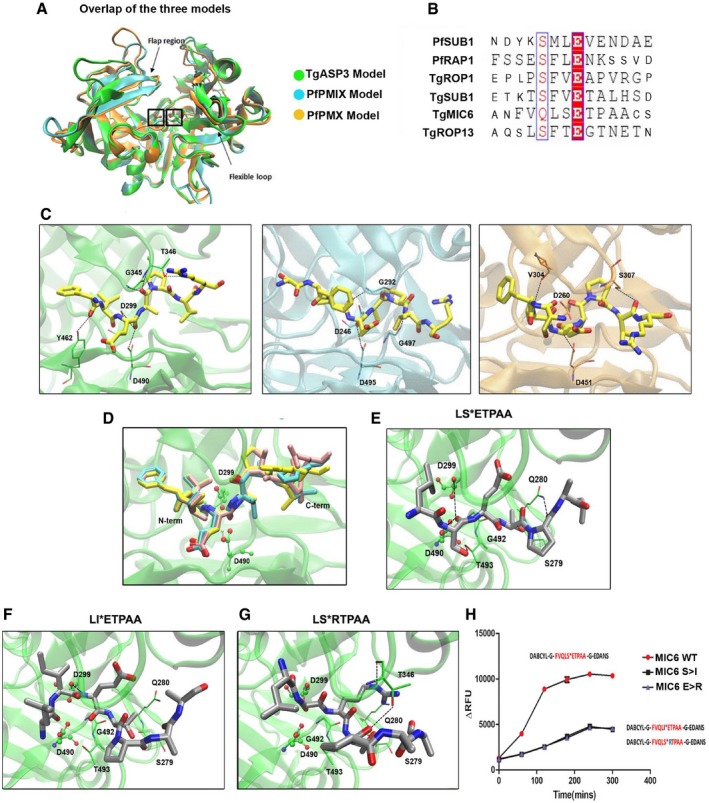
Overlap of the three models: TgASP3 (green), PfPMIX (cyan), and PfPMX (orange). The catalytic aspartyl residues are marked with a box, while arrows indicate the flexible loop and the flap region.
-
B
Sequence alignment of the rhoptry and microneme substrates used for the cleavage assay. Synthetic peptides used in the assay are represented in large font.
-
C
The conserved “productive” binding modes of the substrate TgROP1 (yellow) in the three different proteases active sites. From left to right: TgASP3 (green), PfPMIX (cyan), and PfPMX (orange).
-
D
Overlap of the docking solutions of the three peptides: TgROP1 (yellow), TgROP13 (pink), and TgSUB1 (cyan). All the peptides are represented in licorice with the P1 and
residues colored as atom type (Fig
EV1G).
-
E
Proposed binding mode of TgMIC6 peptide (LSETPAA) in TgAsp3, shown in gray with atom type specified. The side chains of the main interacting residues are reported in licorice with carbon colored in green, and the hydrogen bonds are outlined with black dotted lines.
-
F, G
Docking solutions of TgMIC6 mutant peptides: TgMIC6 S>I (F) and TgMIC6 E>R (G). The side chains of the main interacting residues are shown in green; the hydrogen bonds are outlined with black dotted lines.
-
H
Immunoprecipitated ASP3ty cleaves wild‐type TgMIC6 peptide (DABCYL‐G‐VQLSETPA‐G‐EDANS) more efficiently than TgMIC6 mutant peptides (DABCYL‐G‐VQLIETPA‐G‐EDANS, DABCYL‐G‐VQLSRTPA‐G‐EDANS). Data represent mean ± SEM, n = 3, from a representative experiment out of three independent assays.