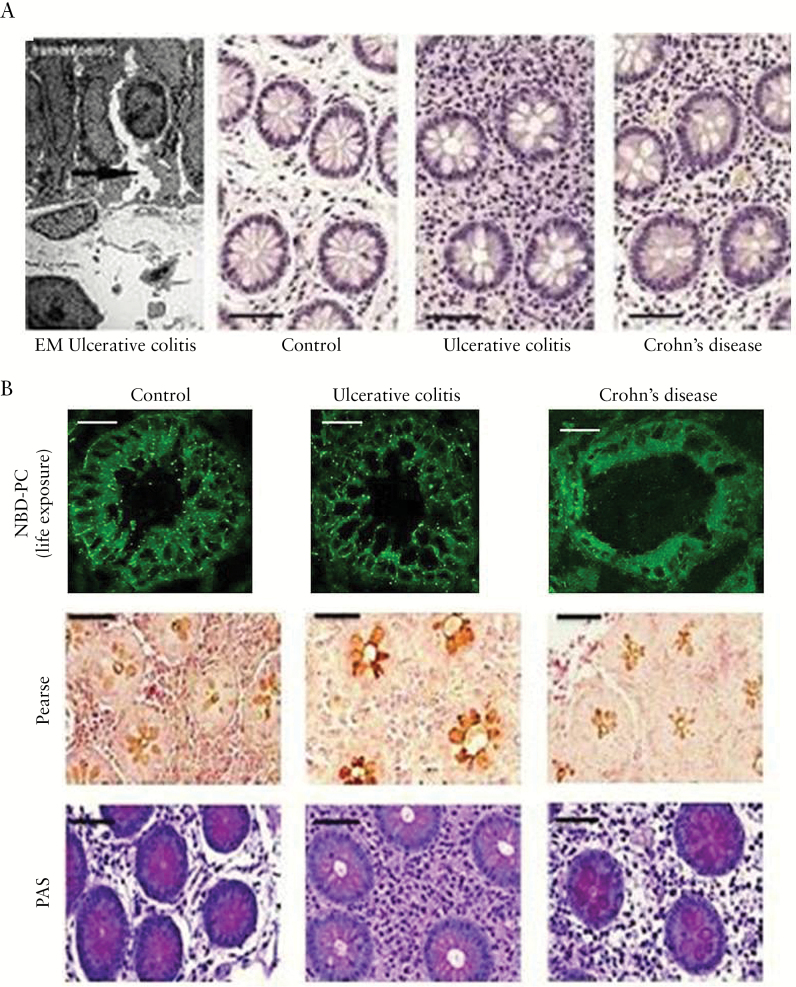
Figure 5.
Widened crypts due to disturbed TJs in human UC [in remission] and consequent impairment of luminal PC accumulation. [A] Electron micrograph of a human UC specimen with epithelial disturbance [arrow shows widening of the intercellular cleft] and HE staining of non-inflamed mucosa with wider crypt lumina in UC patients than in control subjects and patients with Crohn’s disease. [B] [upper panel] NBD-PC live exposure of colonic biopsies showing an impaired paracellular and mucus staining only in UC patients but not in healthy controls and patients with Crohn’s disease. [lower panels] Reduced Pearse and PAS phospholipid staining of samples from UC patients in clinical remission vs. control subjects and patients with Crohn’s disease [scale bars = 25 µm].