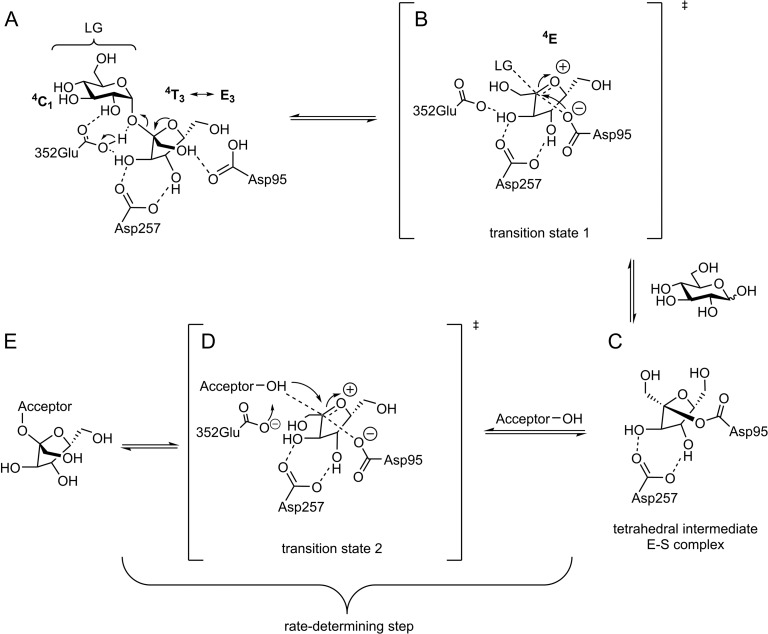
Fig. 2.
Possible reaction pathway of GH68 enzymes. (A) Donor (sucrose in this figure) coordinates in the active site of the enzyme; (B) d-glucose is released and a reactive oxocarbenium ion-like transition state (TS1) of the fructosyl-residue is formed and subsequently attacked by Asp95; (C) a covalent fructosyl-enzyme (ES-complex) complex is formed; (D) the acceptor attacks in the second formed transition state (TS2) to (E) form a fructosylated acceptor (Rye and Withers 2000; Bissaro et al. 2015).