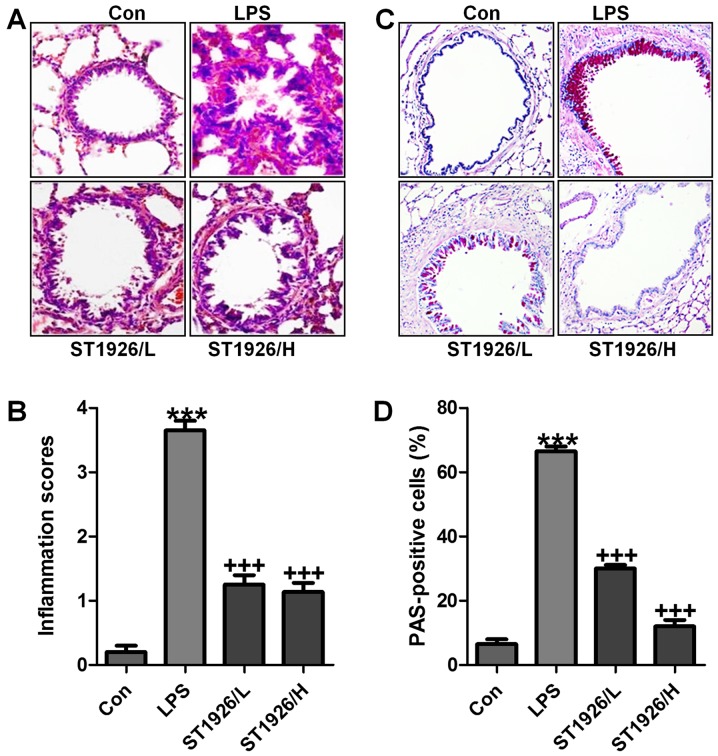
Figure 2.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury in mice is ameliorated by ST1926 administration. (A) The representative images of lung injury are shown by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. (B) The quantification of inflammatory response following H&E staining. (C) PAS staining was used to observe goblet cells in LPS-induced mice with acute lung injury. (D) The quantification of PAS-positive cells. The data are presented as mean ± SD (n=8). *p<0.05 and **p<0.001 vs. the control (Con); +p<0.05, ++p<0.01 and +++p<0.001 vs. LPS-induced mice (LPS).