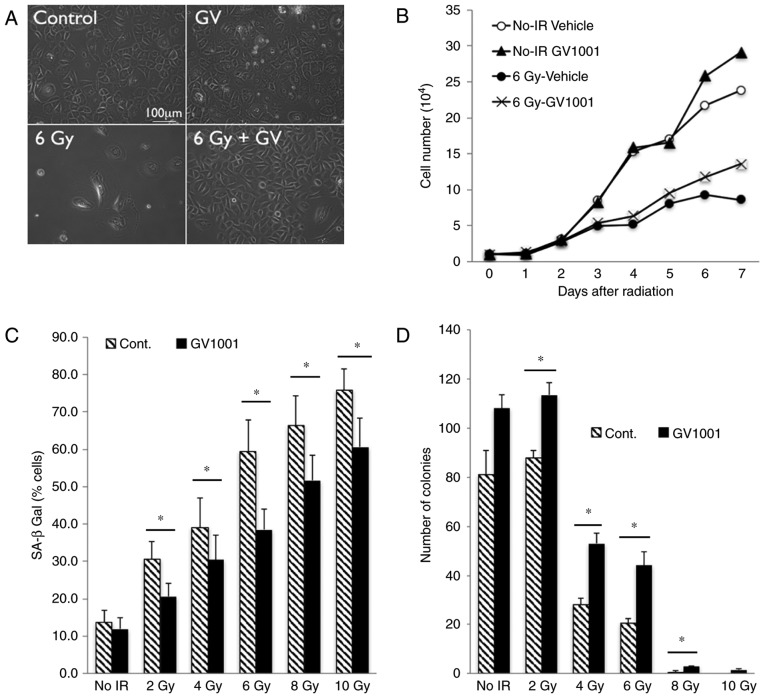
Figure 1.
GV1001 attenuates the IR-induced premature senescence phenotype of NHOKs. (A) Rapidly proliferating NHOKs were exposed to 6 Gy IR and maintained in culture for 10 days in the presence or absence of GV1001 (1 µM) (original magnification, ×100; scale bar, 100 µm; n=3). (B) Cell proliferation kinetics were determined in NHOKs irradiated at 6 Gy IR with GV1001 (1 µM) or vehicle control. (C) NHOKs were exposed to IR at 2–10 Gy in the presence or absence of GV1001 (1 µM) and stained for SA β-Gal. Positively stained cells were counted and plotted. Error bars represent the mean ± standard deviation. (D) NHOKs exposed to 2–10 Gy IR were plated at low density for colony formation in the presence or absence of GV1001 (1 µM). After 10–14 days, the number of colonies were counted and plotted. Error bars represent the mean ± standard deviation. *P<0.05. NHOKs, normal human oral keratinocytes; IR, ionizing radiation; Cont, control; SA β-Gal, senescence-associated β-galactosidase.