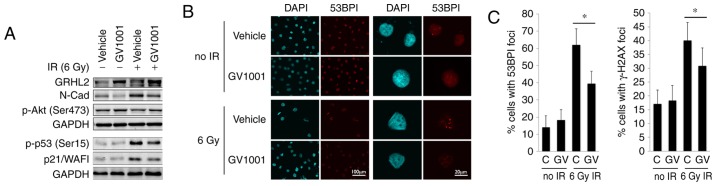
Figure 2.
GV1001 treatment reduces the level of DNA double strand breaks in NHOKs exposed to IR. (A) Western blot analysis was performed with NHOKs 10 days following exposure to 6 Gy IR with or without GV1001 (1 µM) for GRHL2, N-Cad, p-Akt (Ser473), p-p53 (Ser15) and p21/WAF1. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B) NHOKs were exposed to 6 Gy IR in the presence or absence of GV1001 (1 µM), were stained for 53BP1 and were viewed under confocal microscopy to detect 53BP1 intranuclear foci. DAPI staining revealed the nuclei (original magnification of left 2 panels, ×100; scale bar, 100 µm; n=3; original magnification of right panels, ×500; scale bar, 20 µm; n=3). (C) Percentages of cells with 53BP1 or γ-H2AX intranuclear foci (>3 foci per nucleus) were counted in ≥10 various fields from each experiment and plotted. Error bars represent the mean ± standard deviation. *P<0.05. NHOKs, normal human oral keratinocytes; IR, ionizing radiation; GRHL2, Grainyhead-like 2; N-Cad, N-Cadherin; p-, phosphorylated.