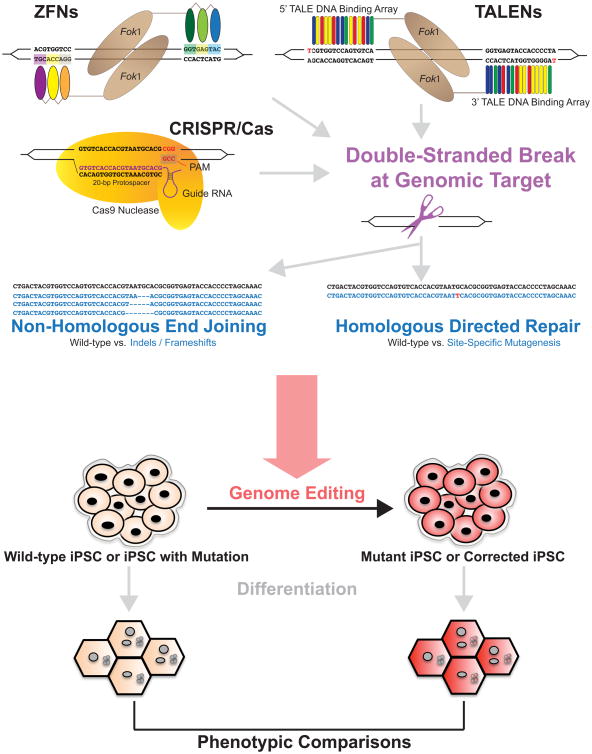
Figure. Overview of genome-editing tools and application to human iPSCs.
ZFNs are a chimeric enzyme that includes a FokI nuclease (brown oval) attached to DNA-binding zinc finger domains (colored ovals) that each interact with 3-4 bp DNA sequences (each group color-coordinated with corresponding zinc finger domain), allowing for recognition of a 9-18 bp genomic sequence when engineered in tandem. The DNA binding domains flank the target genomic site, where the FokI nucleases make a DSB. TALENs are also a chimeric enzyme but with a FokI nuclease attached to a TALE DNA-binding array, which consists of RVDs (colored rectangles) that each bind to genomic DNA in a 1 RVD to 1 bp ratio. The genomic target site is cleaved by the FokI nucleases, which are flanked by the TALE DNA binding array sequences. Note that the 5′ ends of the TALE arrays begin with a thymine. The CRISPR/Cas9 system consists of a guide RNA (purple) binding to the genomic target (20 bp protospacer) and interacting with the Cas9 nuclease (yellow) that recognizes the PAM site. After a DSB is created by one of these techniques, the DNA can undergo (1) NHEJ in which the blunt ends are rejoined with introduction of additional nucleotides that induce an indel/frameshift mutation (dashes) for gene knockout or (2) HDR in which a repair template is introduced to facilitate the incorporation of a specific point mutation (red letter). This overall genome-editing strategy can then be employed to study gene function in iPSCs. iPSCs derived from humans (beige) can either be wild-type from a healthy individual or with mutation from an individual with the disease of interest. Genome-edited iPSCs (red) can be generated through introduction of a mutation to create a mutant iPSC or corrected iPSC, providing the genetic study complement on an isogenic background. These iPSCs can then be differentiated into the cell type of interest for further study of cell-autonomous phenotypes. iPSCs = induced pluripotent stem cells, ZFNs = zinc finger nucleases, DSB = double-stranded break, TALENs = transcription activator-like effector nucleases, RVD = repeat-variable di-residue, NHEJ = non-homologous end joining, HDR = homology-directed repair.