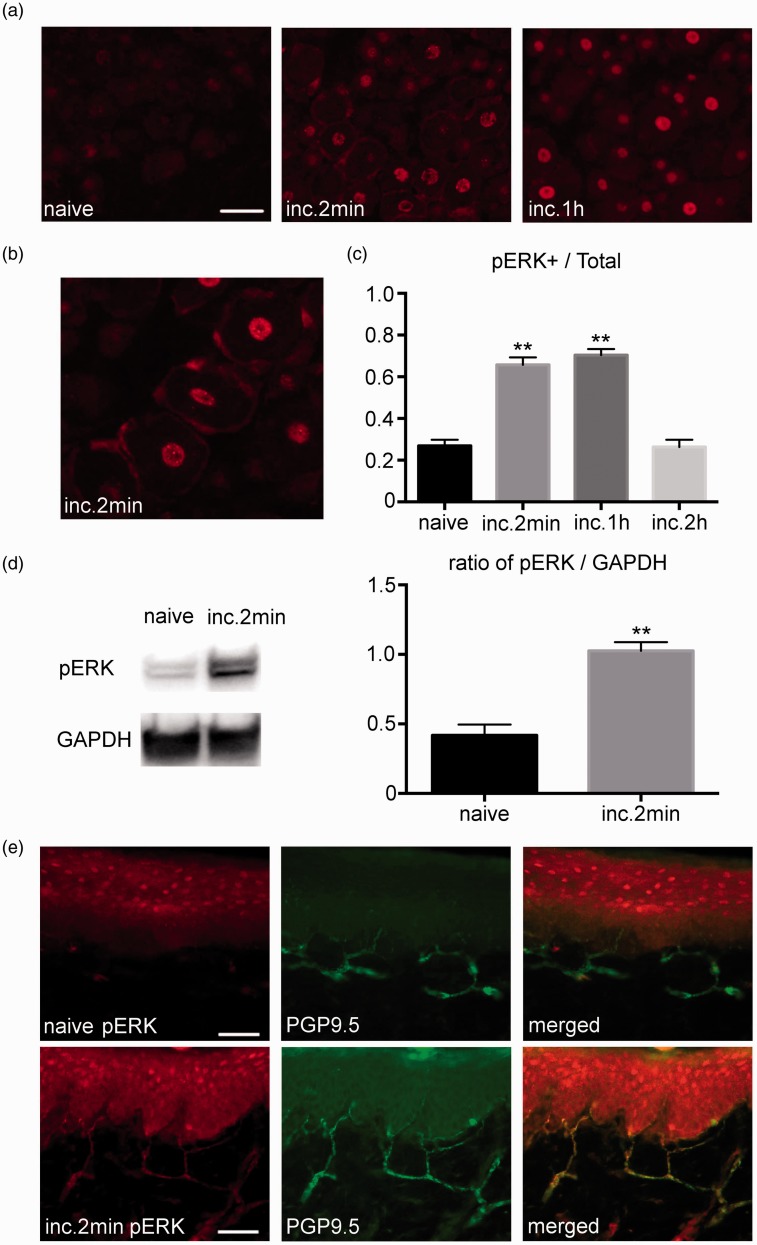
Figure 1.
Expression of pERK1/2 in the DRG and plantar tissue after the plantar incision. (a) Weak pERK1/2 signals were detected in the DRG of the naive group. Robust pERK1/2 expression was detected in the DRG after the incision. Scale bar = 50 µm. (b) Magnified image of the DRG at 2 min after the incision. pERK1/2 was visualized in the neurons and glial cells. (c) There was a significant increase in the number of neurons that express pERK1/2 at 2 min and at 1 h after the incision. The number of pERK1/2 positive neurons returned to baseline at 2 h after the incision. n=5 for each group. ** p<0.01 versus the naive group. (d) There was a significant increase in the amount of pERK1/2 in the DRG measured by Western blotting after the incision. n=5 for each group. ** p<0.01 versus the naive group. (e) Double-labeling immunohistochemistry for pERK1/2 and PGP9.5 in the plantar tissue. pERK1/2 expression was not observed in the naive group. Strong pERK1/2 expression was detected in the PGP9.5 positive nerve endings at 2 min after the incision. DRG: dorsal root ganglion; pERK1/2: phosphorylated ERK1/2.