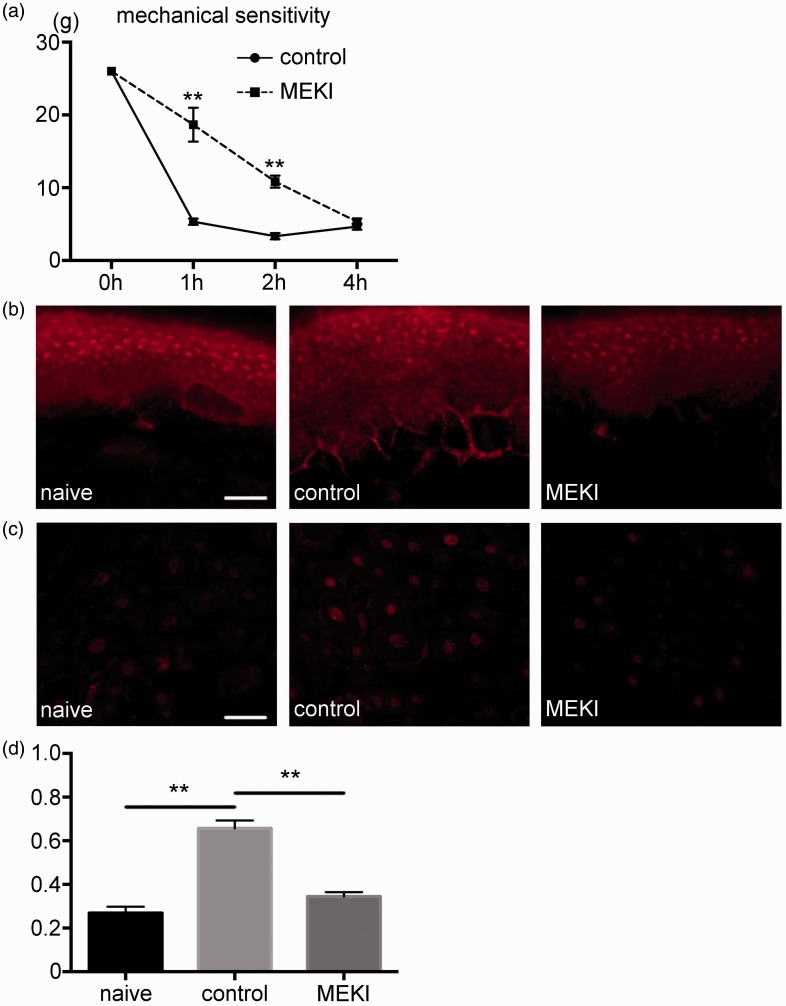
Figure 3.
Inhibition of pERK1/2 reduced pain hypersensitivity after the plantar incision. (a) Behavioral testing results. In the control group, plantar incision induced a decline of the threshold against mechanical stimulation after the incision. The mechanical threshold was significantly higher in the MEK inhibitor group at 1 and 2 h after the incision, as compared to the control group. n=5 for each group. **: p<0.01. versus control group. (b) The effect of MEK inhibitor on pERK1/2 expression in the plantar tissue. pERK1/2 expression in the nerve endings of the plantar tissue was detected in the control group but not in the MEK inhibitor group. Scale bar = 50 µm. (c) The effect of MEK inhibitor on pERK1/2 expression in the DRG. pERK1/2 expression in the DRG reduced in the MEK inhibitor group compared to the control group. Scale bar = 50 µm. (d) The number of pERK1/2 positive neurons was significantly smaller in MEK inhibitor group compared to the control group. **: p<0.01. MEKI: MEK inhibitor; DRG: dorsal root ganglion; pERK1/2: phosphorylated ERK1/2.