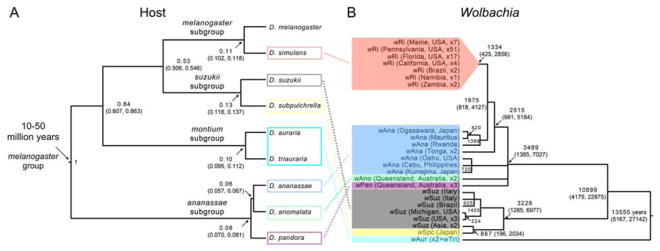
Figure 1. Hosts and their wRi-like Wolbachia.
(A) Bayesian chronogram with relative age estimates (medians and 95% credible intervals) of nodes in the phylogeny for the eight focal Drosophila host species, which span the melanogaster species group, plus D. melanogaster. The estimated age of the melanogaster species group (i.e., the age of the root node) is from [24]. (B) Bayesian chronogram with absolute age estimates (medians and 95% credible intervals) for 110 wRi-like Wolbachia genomes, based on a calibration of rates of Wolbachia divergence from [15]. The chronogram was estimated using complete sequences of 525 single-copy loci present in full length in all 109 draft genomes (506,307 bp), plus the wRi reference. Node ages (see Table S5) are provided only for nodes with posterior probabilities > 0.95 (we collapse nodes with lower probabilities into polytomies). The clade with an inferred age 3489 years (and 95% credible interval (1385, 7027)) includes all of the wRi-like sequences from D. simulans (wRi), D. ananassae (wAna), D. anomalata (wAno) and D. pandora (wPan). Its sister clade has an estimated age of 3228 (1285, 6977) years and includes only the Wolbachia from D. suzukii (wSuz) and D. subpulchrella (wSpc). The wRi sequences occur in a clade that includes eight diverse wAna, consistent with D. ananassae as the source for wRi in D. simulans. These data do not resolve the relationships among the wRi-like Wolbachia in the three ananassae subgroup species, D. ananassae, D. anomalata and D. pandora. The wSpc sequence from D. subpulchrella is nested within the wSuz sequences from its sister species, D. suzukii, suggesting horizontal Wolbachia transfer or introgression from Asian D. suzukii to D. subpulchrella. Our posterior estimate of the MRCA age for these 110 wRi-like variants is approximately 14,000 years, with 95% credible interval (5,000–27,000) years. See also Table S1.