Figure 1.
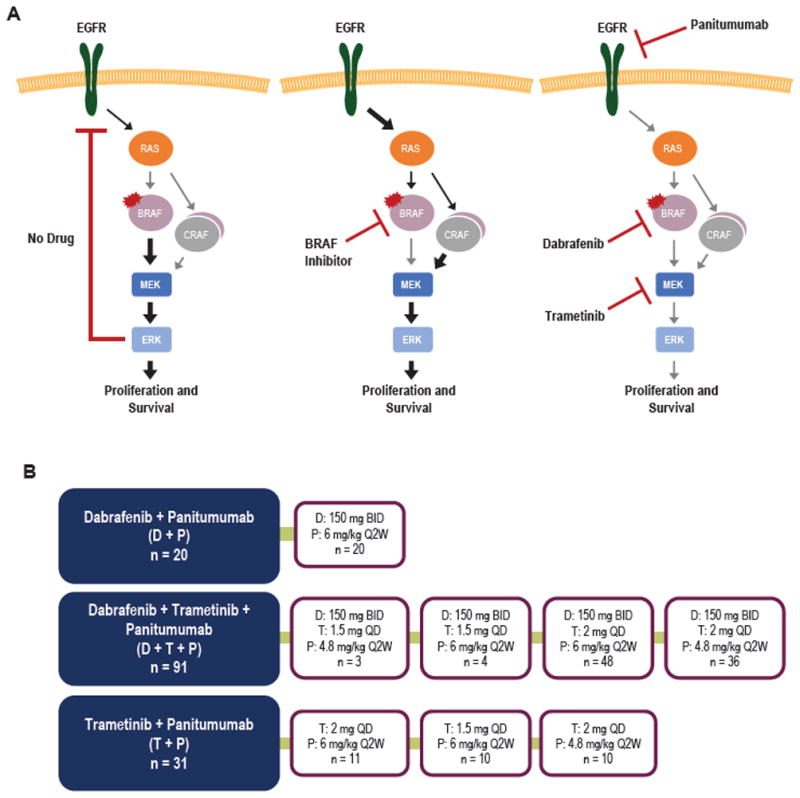
Targeting adaptive feedback signaling in BRAFV600E CRC. A, Model of adaptive feedback signaling in BRAFV600E CRC. Left, In the absence of drug, MAPK activity is driven by mutant BRAF, and ERK-dependent negative feedback signals constrain RTK-mediated activation of RAS. Center, BRAF inhibitor alone leads to transient inhibition of MAPK signaling and loss of ERK-dependent negative feedback signals, allowing RTK-mediated reactivation of the MAPK pathway through RAF dimers (including BRAF and CRAF). Right, Combined inhibition of BRAF, EGFR, and MEK is hypothesized to prevent adaptive feedback reactivation and maintain MAPK pathway suppression. B, Trial schematic showing treatment arms and dosing cohorts for treatment of patients with BRAFV600E CRC. Note that patients treated at doses of dabrafenib 150 mg BID, trametinib 2 mg QD, and panitumumab at 6 mg/kg or dabrafenib 150 mg BID, trametinib 2 mg QD, and panitumumab at 4.8 mg/kg were enrolled into the dose escalation and dose expansion phases of the trial.
