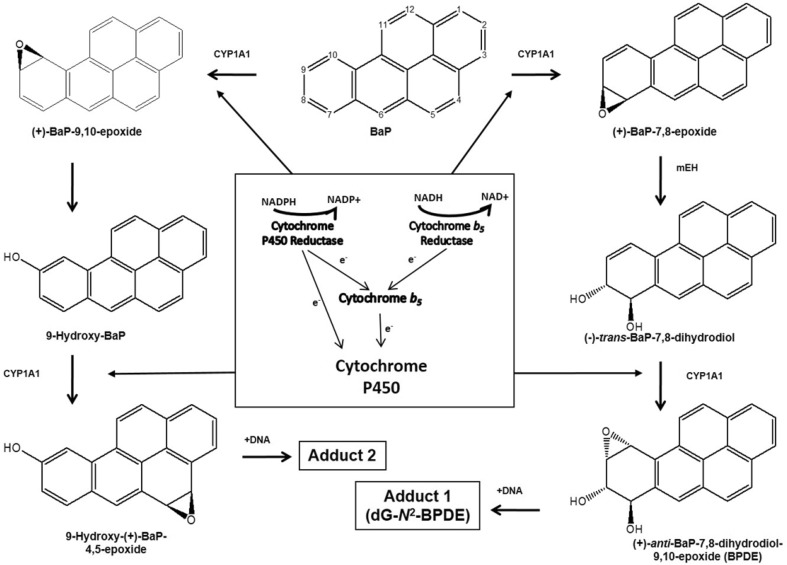
Fig. 1.
Pathways of BaP biotransformation and BaP–DNA adduct formation catalysed by CYP1A1 and mEH. The three-stage pathway, involving mEH, forming the ultimately reactive species BPDE that binds to guanine to form the dG-N2-BPDE adduct (adduct 1) is shown on the right. The two-stage pathway that does not involve mEH forms the second adduct (i.e. adduct 2) seen in in vitro studies is shown on the left; the structure of the adduct has not yet been elicited, the adduct is probably derived from the reaction of 9-hydroxy-BaP-4,5-epoxide with guanine residues in DNA. The diagram in the centre shows the roles of POR, Cyb5R and Cyb5 as electron donors to P450 enzymes such as CYP1A1 that are central to the biotransformation of BaP