Figure 5.
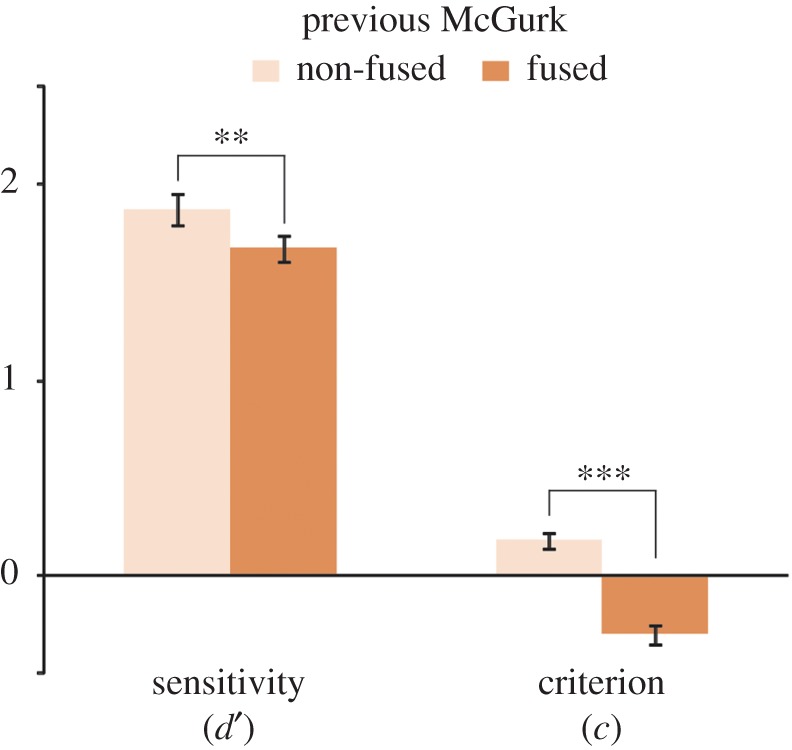
Recalibration depends on perceiving the McGurk illusion. McGurk trials were split into non-fused (‘aba’ percept, light orange) and fused (‘ada’ percept, dark orange) trials. When participants fused the preceding McGurk stimulus, the sensitivity d′ to distinguish /aba/ from /ada/ was smaller compared to when they did not fuse it. After a McGurk illusion, participants gave more ‘ada’ responses (negative criterion shift) while after a non-fused McGurk stimulus, they responded ‘aba’ more often (positive criterion shift). N = 31. (**p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).
