Fig. 1.
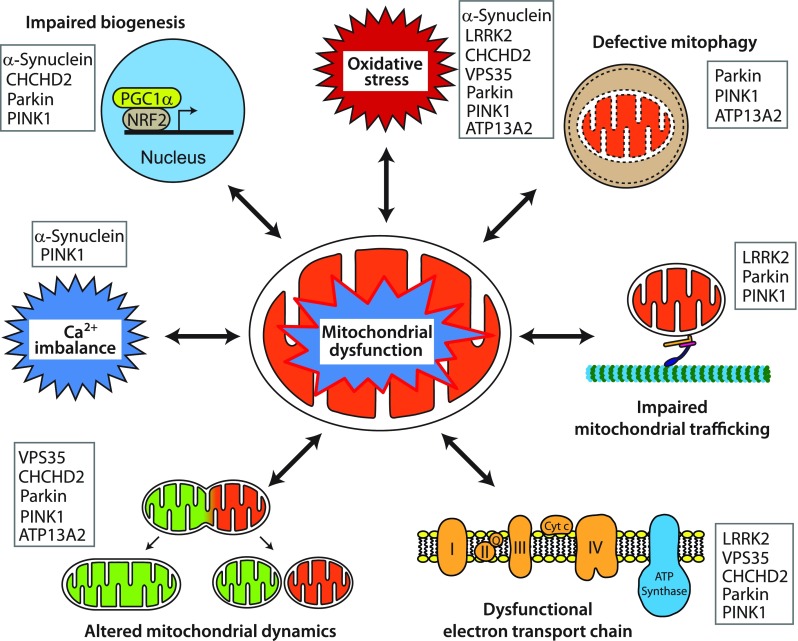
Representative pathways of mitochondrial dysfunction involved in Parkinson’s disease pathophysiology. Mitochondrial dysfunction associated with PD pathogenesis can result from impairment of mitochondrial biogenesis, increased reactive oxygen species production, defective mitophagy, compromised trafficking, electron transport chain dysfunction, variations to mitochondrial dynamics, calcium imbalance or combinations thereof. The potential complex interplay of the various functions leads to a vicious cycle of progressive cellular dysfunction that ultimately results in neurodegeneration that underlies PD pathogenesis and progression. Proteins mentioned in this review that contribute pathologically to the different pathways are listed
