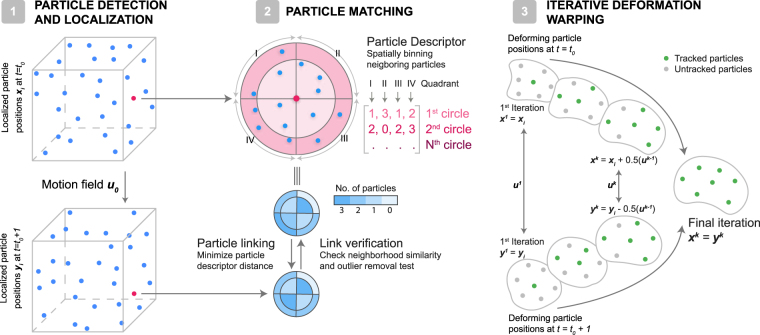
Figure 1.
Schematic of the T-PT algorithm. Step 1: Particles in the images are detected and their centers localized with subpixel accuracy using the radial symmetry method39,40. Step 2: T-PT is a feature-vector-based particle method. Particles are linked via a unique “particle descriptor” or feature-vector, which is created by spatially binning the neighboring particles. The particles are linked one-to-one between consecutive image frames by minimizing the particle descriptor L2 norm distance. These particle links are temporary and are subjected to outlier removal schemes53 to eliminate potential false particle links. The links verified by the outlier removal scheme are converted to actual particle matches. Step 3: Iterative deformation warping51 is used to resolve large particle displacements. Here, the positions of particles in the reference and deformed frames are iteratively warped by a linearized displacement field computed from matched particles, until the positions of the particles in the two consecutive frames coincide. The whole process of particle matching and iterative deformation warping is performed iteratively until a set of convergence criteria is met.