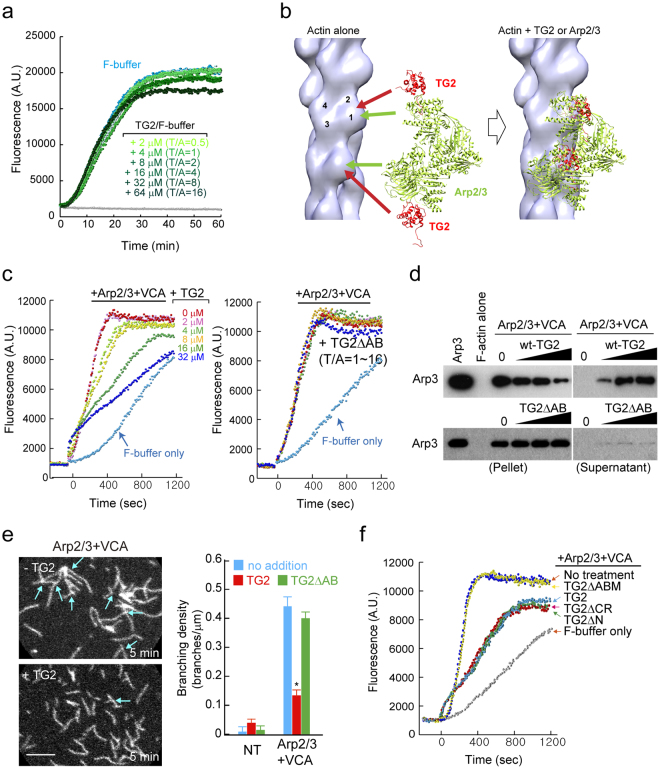
Figure 5.
TAGLN2 inhibits Arp2/3 complex-mediated nucleation of branched filaments. (a) Time-based fluorometric analysis of pyrene-labelled actin polymerization. Polymerization assay in presence of His-TG2 (0, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, and 64 μM) in F-buffer. Results are representative of at least three independent experiments. (b) Fitting of TG2 (red) and Arp2/3 (green) to F-actin reconstruction, showing the clash between TG2 and ARP2/3. (c) Dose-dependent inhibition of Arp2/3 and VCA-stimulated actin nucleation by TAGLN2. (0–32 μM TAGLN2 [TG2] or TAGLN2ΔAB, 20 nM Arp2/3, 200 nM GST_VCA). Results are representative of at least three independent experiments. (d) Competition with the Arp2/3 complex for actin binding in the presence of TAGLN2 or TG2ΔAB. Full-length blots/gels are presented in Supplementary Fig. S7. (e) Real-time imaging of actin branching formed by Arp2/3 and VCA with/without TAGLN2 (left). Scale bars, 2 μm. Quantification of branching density for each condition (right). *p < 0.05 versus no addition. (f) Fluorometric analysis of pyrene-labelled actin polymerization in the presence of the indicated proteins (Note, 2 μM actin, 8 μM TAGLN2 [TG2] or TAGLN2 mutants; 20 nM Arp2/3, and 200 nM GST_VCA). Results are representative of at least three independent experiments.