Figure 1.
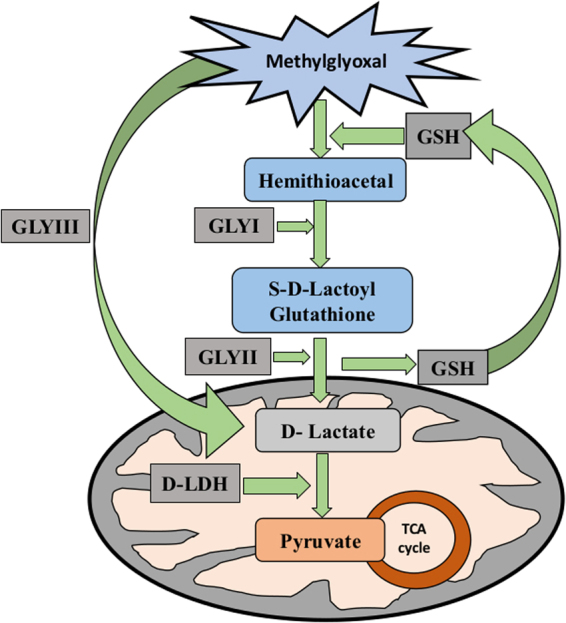
Methylglyoxal detoxification pathway: MG is a toxic metabolite produced in the cell. The detoxification of MG is carried out by various pathways; major one being glyoxalase system that consists of two enzymes, Glyoxalase I and II. Glyoxalase I enzyme converts MG into S-D-lactoyl glutathione which is converted to D-lactate by Glyoxalase II. Glyoxalase III converts MG directly into D-lactate without using any cofactor. Further another enzyme, D-LDH converts this D-lactate into D-pyruvate which goes to TCA cycle. Thus, the toxic MG is diverted to produce energy for the cell.
