Fig. 2.
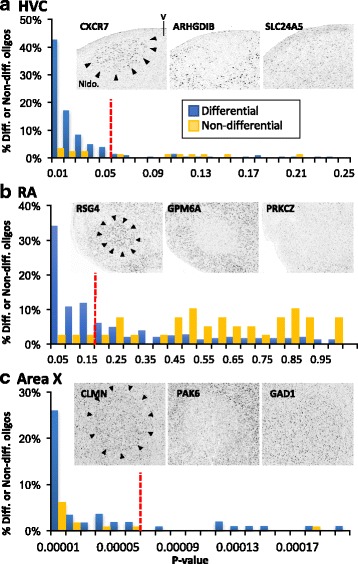
Establishment of Significance Cut-offs For HVC, RA, and Area X Array Studies Based on an Analysis of Gene Expression Patterns in the Zebra Finch Brain Expression Atlas (ZEBrA). Differential (left and middle photomicrographs in A-C) and non-differential genes (example photomicrographs in A-C) were identified for each song nucleus (A-C) by visually analyzing a subset of 320 high resolution in situ hybridization images from the ~ 500 that are available on the ZEBrA finch expression brain atlas (ZEBrA; www.zebrafinchatlas.org; in situ gene lists in Additional File 1: Table S2). For each nucleus, p-value frequency histograms were calculated for sets of oligo that corresponded to differential or non-differential genes, and the histograms were plotted on the same graphs (graphs in A-C). High-confidence p-value cut-offs (dotted lines in the graphs in A-C) were established visually and define p-value cutoffs that capture the highest proportion of true vs. false positives. P-value cutoffs were used to define significant versus non-significant oligos in the subsequent oligo array scoring analysis (see methods for details)
